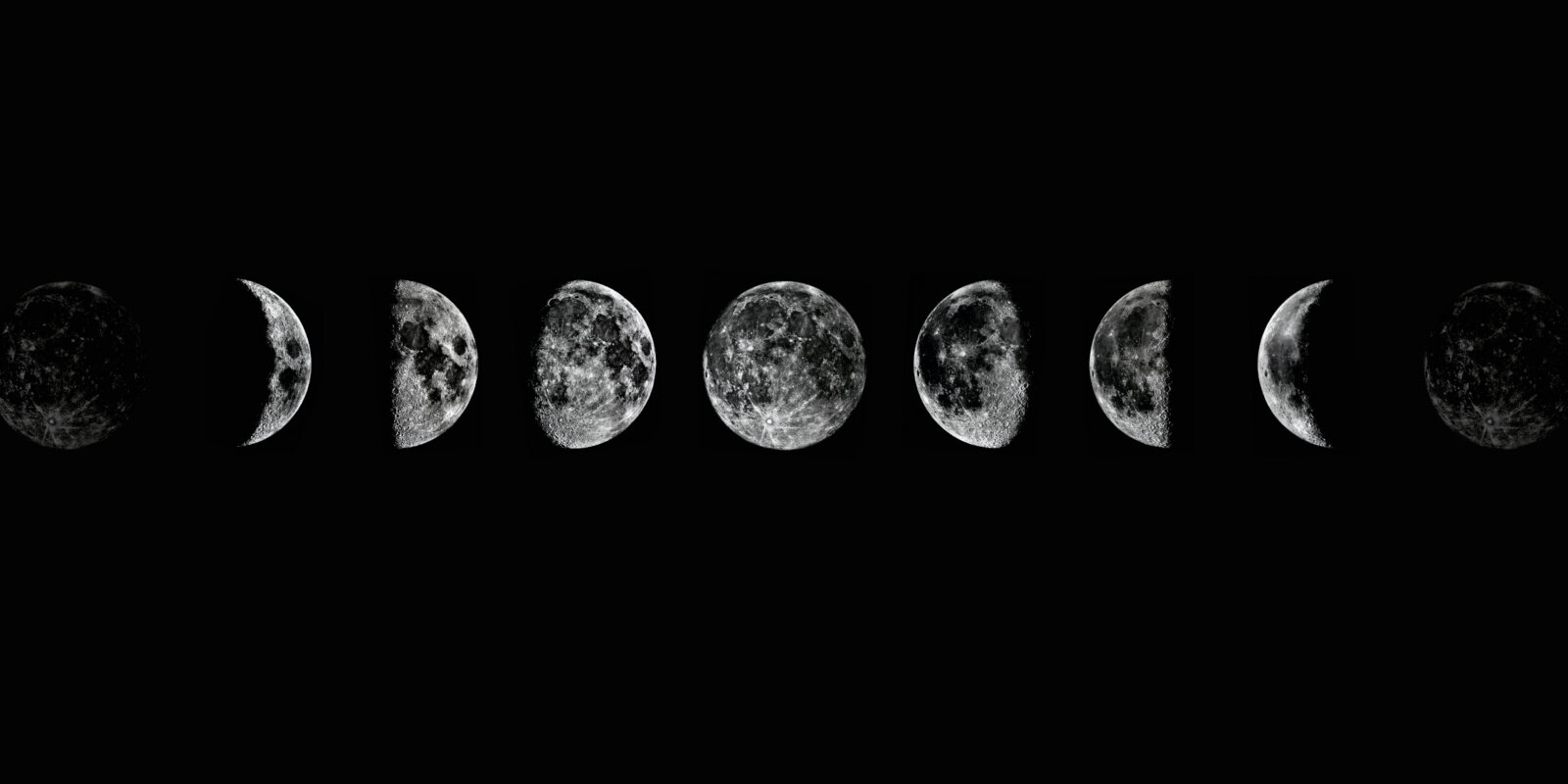
Moon Phases 2022 Calendar – For most dates in the moon phase calendar above, there is a number of days listed below the grid cell, such as “18 days.” It tells us how many days since the last new moon, or in other words, how many days we are in the lunar cycle – aka, the age of the moon.
So at new moon, that day is “0” (not marked); Next day 1 day has passed; And so on until 29 days have passed and we are at the next new moon. You can also find this information in the print edition of The Old Farmer’s Almanac, in the last (right) column of the left calendar pages.
Moon Phases 2022 Calendar
 Source: img.freepik.com
Source: img.freepik.com
This phase gets its name because at this point the Moon has traveled 1/4 of its orbit. However, this is a confusing label as only 1/2 of the Moon’s surface is illuminated from our point of view.
• First Quarter
In fact, the first and last quarter phases are sometimes called moons. At first quarter in the Northern Hemisphere, the right side of the Moon is illuminated; In the Southern Hemisphere it is on the left.
In fact, we only see 1/2 of the illuminated side of the Moon because the entire illuminated surface is only partially facing our direction. In other words, the Moon is perpendicular to the Earth/Sun line. During the first quarter phase, the Moon is said to be in the eastern quadrant, meaning it is 90 degrees east of the Sun as seen from Earth.
This phase occurs between the new moon and first quarter phases. Early in this phase, we see a thin, crescent-shaped moon, visible to the right in the northern hemisphere. The illuminated area gradually expands each day, covering more and more of the right side of the Moon’s surface until the first quarter phase, when the entire right side of the Moon is illuminated.
(In the Southern Hemisphere, the same thing happens, only to the left.) This calendar is a look at the last daily phases of the Moon in January 2022. The month began with the phase published on Saturday, January 1.
• Waxing Crescent
Explore this January moon phase calendar by clicking on each day to see detailed information about the day’s phase. Also see more information about full moon and new moon in January 2022 including local viewing times.
For example, during a waxing moon phase, we may see a thin crescent moon glowing with direct sunlight, but the rest of the lunar disk is also illuminated by a brightness much lower than Earth’s brightness.
This appearance is sometimes referred to as “the old moon in the arms of the new moon”. Sometimes, if the new moon’s position is aligned between the Sun and Earth, it will cover part or all of the solar disk from our view, causing a solar eclipse.
These phenomena are only visible from a small part of the Earth and require special eye protection to view safely. (Read more about solar eclipses here!) The moon phases below are for UTC time, which is the primary time standard that the world uses to set its clocks by adding or subtracting hours as offset time from UTC time.
January – Moon Phase Calendar
does for Note: The synodic month describes the time it takes for the Moon to complete one revolution around the Earth and return to the same position relative to the Sun and Earth. If the Earth did not move in its orbit, but instead remained stationary, the Moon would take less time to reach the same position: this is called a sidereal month, which is about 2.21 days shorter than a synodic month.
“Sidereal” means “relative to the stars”—in this case, the Moon’s position relative to the stars. The term “age of the moon” is not a reference to how long the moon has been around (about 4.5 billion years, in case you were wondering), but rather to how many days have passed since the last new moon.
 Source: griffithobservatory.org
Source: griffithobservatory.org
As mentioned above, the period of time between one new moon and the next is called a lunar cycle, lunar month, lunar month or synodic month and lasts an average of 29.53059 days. This means 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes and 3 seconds.
The 2022 moon phase calendar below shows both your local time zone as well as (UTC) Coordinated Universal Time in Jakarta Raya/Jakarta. Dates and times provided have been adjusted to reflect time zones, daylight saving time and other adjustments as necessary.
What Is The Moon’s Age?
The number of moons counts the time between one new moon and the next new moon (full cycle) which is approximately 29.53 days. It is the journey of the Moon as it orbits the Earth that creates a predictable dance between light and shadow.
And while the changes may seem slow, the amount of moonlight illuminated by the sun on any given day can vary by up to 10 percent. The illustration above shows the light range for today – March 3, 2023.
The image is set to your computer’s clock and therefore gives you the correct reading for your own time zone. © 2011 – 2023 7Graus – Calendarr.com Online calendar with holidays and celebrations. We say “necessarily” for the quarter phases because technically, at the exact time of the first quarter, a little more than half of the moon is illuminated, and a little less in the last quarter.
. The moon is fully half-illuminated when it reaches bifurcation, which is several minutes before first quarter and several minutes after last quarter. Let’s start with some interesting facts. It takes 29.53 days for the Moon to complete a full lunar cycle around the Earth.
Moon Calendar Dates And Times
During this period the moon will go through every phase. Because the Moon’s orbital journey takes slightly less than a full month, you’ll notice that when you click on future dates, the full moon occurs a day or two earlier each month, depending on the exact number of days in that month.
. This phase is so named because it begins a new lunar cycle. At this time, the Sun and Moon are in conjunction, which means they are closest to each other in the sky on the same
side of the Earth (Sun → Moon → Earth).
From our point of view, the Moon appears completely dark: we normally can’t see it because we face the shadow side of the Moon, which doesn’t get direct sunlight. But if we travel to the other side of the moon, the part facing the sun, it will be completely illuminated.
The percentage illuminance, listed in the moon phase calendar under the moon sign, tells us how illuminated the moon’s disk is, as seen from Earth. Looking at the calendar on this page, you can see that from new to full, the percentage increases, which represents the waxing phases, and from full to new, the percentage decreases, which represents the waning phases.
Understanding Moon Phases
The New Moon is 0 percent illuminated (or completely dark); The first quarter is essentially 50 percent light (the counter is half light); The full moon is 100 percent illuminated (the entire disc is illuminated); And the last quarter is essentially back to 50 percent light (half is counter light).
This phase gets its name because at this point the Moon has traveled 3/4 through its orbit, and has only one (last) quarter to complete one revolution. This stage is sometimes called the third trimester. At this stage we see 1/2 of the moon’s surface illuminated.
![]() Source: render.fineartamerica.com
Source: render.fineartamerica.com
In the Northern Hemisphere, the left side is illuminated; In the Southern Hemisphere it is to the right. During a last quarter phase, the Moon is said to be in the western quadrant, meaning it is 90 degrees west of the Sun as seen from Earth.
As the Moon revolves around the Earth and the Earth revolves around the Sun, the angle between the Sun, Moon and Earth changes. As a result, the amount of sunlight reflected from the moon and traveled to our eyes varies from day to day.
What Is Percent Illumination?
(The Moon itself does not produce any light of its own.) The length of a lunar cycle can exceed 13 hours due to certain factors. For example, when the new moon phase occurs around the same time as perigee (the point in the moon’s elliptical orbit closest to Earth), small moons result.
When the new moon phase occurs around the time of apogee (when the moon is farthest from Earth), a long moon occurs. This is related to the fact that the Moon moves fastest in its orbit at perigee and slowest in its orbit at apogee.
Astronomers divide this cycle into four primary lunar phases: New Moon, First Quarter, Full Moon, and Last Quarter. There are also four secondary phases: waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous and waning crescent. Primary phases occur at a specific moment, wherever you are on Earth, which is then converted to local time.
(Depending on where you live, you may not be able to see the exact moment of a phase, in part because the moon may not have risen yet in your area.) However, secondary phases Refers to a period of time rather than a specific one.
• Last Quarter
Moments This phase occurs between the last quarter and the new moon phase. At the beginning of this phase, in the Northern Hemisphere, we see the entire left side of the Moon almost completely illuminated and the right side dark.
The illuminated area gradually shrinks each day, covering less and less of the Moon’s surface until it looks like a very thin crescent on the left. Eventually the entire disc will be in darkness, then it will be the new moon phase and a new moon cycle will begin.
(The same thing happens in the Southern Hemisphere, only the illuminated area will have started on the right and shrunk from left to right, until a thin crescent remained on the right.) When the sun first rises, it is easier
does not happen Look at this vulnerable phase; The best time is before sunrise. Sometimes, if the position of the full moon coincides with the Sun and the Earth, from our point of view, the Moon will enter the Earth’s shadow, which will cut off some or all of the Sun’s light reflecting off the Moon’s surface, thus creating a lunar eclipse.
What Are Moon Phases?
Eclipses (read more about lunar eclipses here!) Earthglow is sunlight weakly illuminating the dark part of the Moon’s surface that is directly in front of us. It occurs when light travels from the Sun to the Earth, reflects off the Earth, travels to the Moon, and then bounces back to the Earth to reach our eyes.
When this happens, we can see a part of the Moon that is not normally illuminated, but this part is much less than the part directly illuminated by sunlight. In some cases, lunar and other times may be lost because they do not apply.
 Source: ih1.redbubble.net
Source: ih1.redbubble.net
For example, the moon may not rise and set every day (especially at high latitudes). Also, while the sun always sets after sunrise on the same day, the moon can set in the morning and rise in the afternoon because the lunar cycle is not based on the Earth’s day.
We see the Moon’s disk change from completely dark to completely dark: this period of time is called a lunar cycle, lunar month, lunar month or synodic month. The cycle length can vary slightly, but on average it is 29.53059 days.
• Waning Crescent
(See “What is the age of the moon?” below for more information.) You are using a browser that does not support SVG. This page relies heavily on SVG and other features that are not supported in older browser versions.
This phase occurs between the first quarter and the full moon and describes the moon when it is more than half lit, but not yet fully lit. At the beginning of this phase in the Northern Hemisphere, we see the right half of the Moon illuminated and a small portion extending to the left.
As the days pass, the light moves further to the left, covering the surface of the moon until the full moon phase, when the entire disk
is illuminated. The same thing happens in the Southern Hemisphere, only from left to right.
This phase is between full and last quarter and describes the moon when it is more than half lit, but not fully lit. At the beginning of this phase in the Northern Hemisphere, we see a disk almost completely illuminated, which is dark, except for a small sliver to the right.
What Is Earthshine?
As the days pass, the illuminated area shrinks from right to left until the last quarter phase, when the left half of the Moon is illuminated and the right half is in darkness. The same happens in the Southern Hemisphere, only the light shrinks from left to right.
Below are general guidelines for where to find the Moon in each of its phases. The time stated is solar time, not clock time. The four primary phases (in italics) rise and set at a point;
ਚਾਰ ਸੈਕੰਡਰੀ ਪੜਾਅ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਮਿਆਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਾਪਰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਇਸ ਪੜਾਅ ਦਾ ਨਾਮ ਇਸ ਲਈ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ, ਸਾਡੇ ਦ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਟੀਕੋਣ ਤੋਂ, ਪੂਰੀ ਡਿਸਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਸ਼ਮਾਨ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਸਮੇਂ, ਸੂਰਜ ਅਤੇ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਨ, ਮਤਲਬ ਕਿ ਉਹ ਧਰਤੀ ਦੇ ਉਲਟ ਪਾਸੇ, ਅਸਮਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਦੂਰ ਹਨ (ਸੂਰਜ → ਧਰਤੀ → ਚੰਦਰਮਾ)।
ਪੈਰੀਹੇਲੀਅਨ ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਧਰਤੀ ਦੀ ਸਾਪੇਖਿਕ ਸਥਿਤੀ (ਸੂਰਜ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਨੇੜੇ ਧਰਤੀ ਦੇ ਚੱਕਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਿੰਦੂ) ਅਤੇ aphelion (ਜਦੋਂ ਧਰਤੀ ਸੂਰਜ ਤੋਂ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਦੂਰ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ) ਵੀ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ।
• Waxing Gibbous
ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਲੰਬੇ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਉਦੋਂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਦੋਂ ਨਵਾਂ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਐਪੋਜੀ ਨਾਲ ਮੇਲ ਖਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਧਰਤੀ ਪੈਰੀਹੇਲੀਅਨ ‘ਤੇ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਛੋਟਾ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਉਦੋਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਦੋਂ ਨਵਾਂ ਚੰਦ ਪੈਰੀਜੀ ਨਾਲ ਮੇਲ ਖਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਧਰਤੀ aphelion ‘ਤੇ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ।
ਕੁਝ ਚੰਦਰ ਅਤੇ ਚੰਦਰ ਸੂਰਜੀ ਕੈਲੰਡਰ, ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਇਸਲਾਮੀ (ਜਾਂ ਹਿਜਰੀ) ਕੈਲੰਡਰ, ਇੱਕ ਮਹੀਨੇ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਨੂੰ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਪਰਿਭਾਸ਼ਿਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਦੋਂ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਵਾਰ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਚੰਦ ਦੇ ਇੱਕ ਦਿਨ ਜਾਂ ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਇਸਦੇ ਮੋਮ ਦੇ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ।
ਨੋਟ: ਕਈ ਵਾਰ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਦੋ ਦਿਨਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਸੂਚੀਬੱਧ ਪੂਰਨਮਾਸ਼ੀ ਦੇਖੋਗੇ। ਇਹ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਦਿਨ ਦੇ ਅੰਤ ਅਤੇ ਅਗਲੇ ਦਿਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਦੇ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਦੇ ਸਿਖਰ ‘ਤੇ ਪਹੁੰਚਣ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਪੀਕ ਰੋਸ਼ਨੀ ਕਈ ਵਾਰੀ ਦਿਨ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ।
ਜੇਕਰ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਸਾਲ ਭਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਰ ਪੂਰਨਮਾਸ਼ੀ ਬਾਰੇ ਹੋਰ ਜਾਣਨਾ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਹੋ, ਤਾਂ ਸਾਡੇ ਪੂਰੇ ਚੰਦਰਮਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਤਾਰੀਖਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਾਂ ਪੰਨੇ ‘ਤੇ ਜਾਓ।
• Waning Gibbous
2022 new moons and full moons, moon schedule 2022, printable moon phase calendar 2022, full moon time and date, moon phases 2022 lunar calendar, lunar phase calendar, lunar calendar 2022, was there a full moon last night

