2022 Calendar With Moon Phases – Most of the dates in the moon phase calendar above have several days listed at the bottom of the grid cells, such as “18 days.” It tells us the number of days since the previous new moon, i.e. how many days we are in the lunar cycle, or the age of the Moon.
Therefore, the day of the new moon is “0” (no label); the next day 1 day passed; 29 days pass and we have the next new moon. You can also find this information in the Old Farmer’s Almanac edition, in the last (right) column of the Left Hand Calendar page.
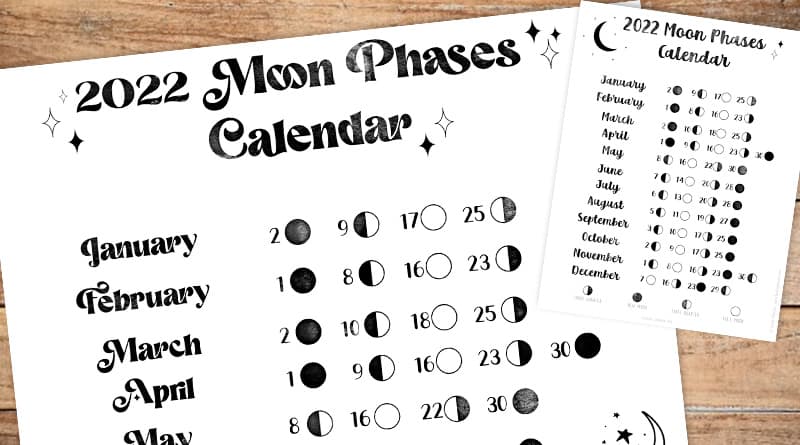
2022 Calendar With Moon Phases
 Source: ourcrazyadventuresinautismland.com
Source: ourcrazyadventuresinautismland.com
This phase is so called because it marks the beginning of a new lunar cycle. Right now, the Sun and Moon are conjunct, meaning they are closest to the sky and on the same side of the Earth (Sun→Moon→Earth).
• Waning Crescent
From our point of view, the moon looks completely dark: we are facing the dark side of the moon, which does not receive direct sunlight, so we usually cannot see it. But if we travel to the other side of the moon, the side facing the sun, it will be fully illuminated.
Sometimes, if the new moon’s position is exactly right between the Sun and the Earth, it covers part or all of the Sun’s disk, causing a solar eclipse. These events are visible to only a tiny fraction of the world and require special eye protection to be seen safely.
(Read more about solar eclipses here!) Each phase rises above the eastern horizon and sets below the western horizon at different times of the day and night. Depending on the phase and timing of moonrise or moonset, the moon may not be visible at the time of rising or setting, but the appearance or non-appearance follows a predictable and observable pattern.
This phase occurs between the last quarter and the new moon. At the beginning of this phase, in the northern hemisphere, we see the entire eastern side of the moon almost fully illuminated, while the western side is in darkness.
Moon Phases In History
The bright area gradually narrows every day, gradually covering the surface of the moon, and on the left side it appears as a very thin crescent. Eventually, the entire disc will go dark, at which point a new moon phase will begin and another lunar cycle will begin.
(The same thing happens in the Southern Hemisphere, only the bright part starts in the west and wanes from east to west, leaving a thin crescent in the west.) Once the sun rises, it’s not so easy.
this subtle phase; the best time is before sunrise. This stage is so called because, in our opinion, the entire disk is illuminated. Right now, the Sun and Moon are in opposition, meaning they are farthest away in the sky and on the opposite side of the Earth (Sun→Earth→Moon).
Some lunar and solar calendars, such as the Islamic (or Hijri) calendar, define the onset of a new moon as the first sighting of the moon, usually one day after the new moon or waxing crescent.
• Last Quarter
Sometimes, if the full moon’s position is perfectly aligned with the Sun and the Earth, the Moon will enter the Earth’s shadow, which blocks some or all of the sunlight from the Moon’s surface, causing a lunar eclipse.
(Learn more about lunar eclipses here!) A full lunar cycle begins with a new moon and then goes through seven different phases before returning to a new moon phase. During the New Moon phase, the Moon is between the Sun and the Earth.
 Source: static1.squarespace.com
Source: static1.squarespace.com
The side facing the Earth is not illuminated by the sun, it is so bright outside that we do not see it. Additional graphs show the Moon’s orbit, subsolar and subterrestrial points, and the Moon’s distance from Earth to a realistic scale.
Craters near the Terminator mark the Apollo landing site, maria and other albedo features in the sun. In this phase, the moon has traveled 3/4 of its orbit and only a (last) quarter remains to complete one revolution, hence this phase gets its name.
• First Quarter
This stage is sometimes called the Third Quarter. At this stage, we see half of the lunar surface illuminated. In the northern hemisphere the eastern side shines; In the southern hemisphere, it is in the west.
During its last quarter phase, the Moon is said to be in the west quadrant position, meaning it is 90 degrees west of the Sun as seen from Earth. You are using a browser that does not support SVG.
Older versions of browsers on which this page relies on SVG and other unsupported features. We see the lunar disk change again from all darkness to all light to all darkness: this period is called the lunar cycle, lunar month, lunar month or synodic month.
Cycle length may vary slightly, but the average is 29.53059 days. (See “How old is the moon?” below for more information.) This phase is so called because the moon traveled 1/4 of its orbit during this phase.
January – Moon Phase Calendar
This is a confusing label, because right now, as we can see, 1/2 of the lunar surface is illuminated. In fact, the first and last quarter phases are sometimes called half moons. In the first quarter of the northern hemisphere, the west side of the moon shines;
In the southern hemisphere, it’s the eastern side. In reality, we see only 1/2 of the illuminated part of the moon, because the entire illuminated surface is only partially directed in our direction. In other words, the Moon is perpendicular to the Earth/Sun line.
During the first quarter phase, the Moon is left square, meaning it is 90 degrees east of the Sun as seen from Earth. Before cutting anything, students should use their knowledge of the moon to shade the phases according to the labels on the moon phase wheel.
Teach the lesson about phases of the moon first to give students the basic knowledge they need to keep a moon journal or complete this step. Students can use their knowledge of the phases of the moon to create a
printable moon phase calendar and calculator.
What Is The Moon’s Age?
They can use this tool to look up the phases of the moon on any day of the year and predict when and where the moon will appear. This calendar is an overview of the past daily moon phases for January 2022. This month started with a bright phase on Saturday January 1st.
Check out the January Moon Phase Calendar and click each day to see phase details for those days. Also, see full and new moon details for January 2022, including local viewing times. The term “age of the moon” doesn’t refer to how long the moon has been around (about 4.5 billion years, in case you’re wondering), but how many days have passed since the last new moon.
 Source: i.pinimg.com
Source: i.pinimg.com
As mentioned above, the period between one new moon and the next is called the lunar cycle, moon, new moon or synodic month, and lasts an average of 29.53059 days. This translates to 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes and 3 seconds.
Explanation: A lunar synod is the time it takes for the Moon to complete one orbit around the Earth and return to the same position relative to the Sun and the Earth. If the Earth were not moving in its orbit, but instead were stationary, the moon would take less time to reach the same position: this is called a sidereal month, which is 2.21 days shorter than a synodal month.
What Is Earthshine?
“Sidereal” means “relative to the stars”, in this case the position of the moon relative to the stars. Terrestrial light is sunlight that slightly illuminates the dark side of the lunar surface in front of us.
It occurs when light travels from the Sun to the Earth, reflects off the Earth, travels to the Moon, and then returns to Earth to reach our eyes. In this case we can see the part of the moon that is not normally illuminated, but this part is much less bright than the part that is directly illuminated by the sun.
Astronomers have divided this cycle into four main lunar phases: new moon, first quarter, full moon and last quarter. There are also 4 sub-phases: waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning crescent and waning crescent. The primary phases occur at specific times anywhere in the world, which are then converted to local time.
(Depending on where you live, the moon may not have risen in your area yet, so you may not be able to see the exact moment of the phase.) But the sub-phases represent periods of time.
Moon Calendar Dates And Times
more than a certain time. The 2022 moon phase calendar below shows both the Jakarta Raya/Jakarta local time zone and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The dates and times provided are adjusted according to time zone, daylight saving time and other settings as needed.
The number of moons is the time period (complete cycle) from one new moon to the next, which is approximately 29.53 days. We say “mostly” for the phases of the seasons, because technically more than half of the moon shines during the first quarter and only a fraction of it shines during the last quarter.
The moon is exactly half-bright when it reaches its dichotomy, which occurs a few minutes before the first quarter and a few minutes after the last quarter. This phase occurs between the new moon and the first quarter.
Early in this phase, we see a narrow crescent-shaped moon appearing in the Western Hemisphere. The illuminated area gradually expands every day, covering more and more of the western side of the lunar surface until the first quarter, when the entire western side of the moon is illuminated.
• Waxing Crescent
(The same thing happens in the southern hemisphere, only on the left side.) Let’s start with some interesting facts. The moon takes 29.53 days to complete a full lunar cycle. During this time, the moon will go through each phase.
Since the moon takes less than a full month to orbit, when you click future dates, you’ll notice that the full moon occurs a day or two before each month, depending on the exact number of days in that month.
 Source: lovelyplanner.com
Source: lovelyplanner.com
The brightness percentage listed in the moon phase calendar under the moon sign indicates how bright the lunar disk is as seen from Earth. From the calendar on this page, you can see that the percentages increase from new to full, indicating a baseline, and the percentages from full to new decrease, indicating a downward phase.
The new moon is 0 percent light (or completely dark); The first quarter is essentially 50% bright (half of the disc illuminated); The full moon is 100% bright (the entire disk lights up); Last season it was pretty much 50 percent lit (half of the puck lights up).
Understanding Moon Phases
Below are general guidelines on where to look for the moon in each phase. The time mentioned is sundial, not clock time. Four main phases (italics) rise and fall over time; The four secondary stages are more extensive.
This phase occurs between the first quarter and full moon and describes the moon when it is brighter than half the moon but not full. At the beginning of this phase in the Northern Hemisphere, we see the western half of the moon illuminated and somewhat more extended to the left.
As the day progresses, light creeps east until it covers the surface of the moon until full moon, illuminating the entire disk. The same thing happens in the southern hemisphere, only from east to west. It’s the moon’s journey around the Earth that creates a predictable dance of light and shadow.
The changes may seem slow, but on any given day, the amount of sunlight illuminated by the moon can change by as much as 10%. The image above shows the brightness range for today – March 03, 2023. The image is adjusted to match your computer clock to give you the correct reading for your time zone.
What Is Percent Illumination?
This phase occurs between full and last quarter and is depicted when the moon is more than half lit, but not full. At the beginning of this phase in the northern hemisphere, we see a disk that is almost completely illuminated, except for a small band of darkness on the right side.
As the day progresses, the illuminated area dec
reases from west to east until the last quarter, when the east side of the moon is bright and the west side is dark. The same thing happens in the southern hemisphere, only the light decreases from east to west.
The phases of the moon below are for UTC, which is the primary time standard used by countries around the world to set the time by adding or subtracting a time difference from UTC. Earth’s relative position near perihelion (the point in Earth’s orbit closest to the Sun) and aphelion (when the Earth is furthest from the Sun) affect lunar timing.
The longest moon occurs when the new moon coincides with the zenith and the Earth is at perihelion. The shortest moon occurs when the new moon coincides with perigee and the Earth is at aphelion. The phases of the moon are the varying amounts of brightness seen on the moon from our perspective on Earth.
When Does The Moon Rise And Set?
They are the result of the relative positions of the Sun, Moon and Earth, with the Moon orbiting our planet in about 29.5 days. As the Moon goes around the Earth and the Earth goes around the Sun, the angles of the Sun, Moon and Earth change.
As a result, the amount of sunlight that reflects off the moon and reaches our eyes changes every day. (The Moon itself emits no light.) For example, during the waxing crescent phase, we can see a thin crescent moon that is brightly illuminated by direct sunlight, but the rest of the lunar disk is slightly obscured by Earth’s rays.
Sometimes this image is called “the old moon in the arms of the new moon.”
moon phases 2022 lunar calendar, lunar calendar 2022, lunar cycle calendar 2022, moon phases time and date, lunar moon phases 2022, calendar with phases of moon, 2022 lunar phases, moon phases today

