Depo Provera Perpetual Calendar – Although Depo-Provera CI should not be used during pregnancy, there appears to be an increased or decreased risk of birth defects in women inadvertently exposed to medroxyprogesterone acetate injections in early pregnancy. Children exposed to medroxyprogesterone acetate in utero and postadolescent infants had no evidence of adverse effects on their health, including physical, mental, sexual, or social development.
To ensure that the patient does not become pregnant at the time of the first injection, the first injection should only be given during the first 5 days of a normal menstrual cycle. Only in the first 5 days after childbirth, if not breastfed;
Depo Provera Perpetual Calendar
 Source: i1.rgstatic.net
Source: i1.rgstatic.net
And if only breast milk is given, then only in the sixth postpartum week. Depo-Provera CI is not indicated before menstruation. Use of Depo-Provera CI is associated with significant loss of BMD. This loss of BMD is of particular concern during adolescence and early adulthood, a critical period of bone growth.
Pediatric Use
For adolescents, the patient’s age and skeletal maturity should be taken into account when interpreting BMD results. It is not known whether taking Depo-Provera CI in young women will reduce bone mass and increase the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures later in life.
In addition to concerns about BMD reduction, safety and efficacy are expected to be similar in postmenarcheal adolescents and adult women. Do not re-inject Depo-Provera CI pending investigation if there is sudden partial or complete loss of vision or sudden proptosis, diplopia, or migraine.
Do not re-inject if papilledema or retinal vascular lesions are detected on examination. When switching from other contraceptive methods, Depo-Provera CI should be administered in such a way as to provide continuous contraceptive coverage based on the mechanism of action of both methods (eg, with oral contraceptives).
Provera CI the day after the last active pill or the day after the last, last inactive pill). The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Depo-Provera CI has not been studied. Depo-Provera CI should not be used by women with significant liver disease and should be discontinued if jaundice or liver problems occur.
Hepatic Impairment
[See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7).] Women with a history or history of breast cancer should not use hormonal contraceptives, including Depo-Provera CI, because breast cancer is hormonally sensitive. May be sensitive to [see
Contraindications (4)]. Women with a family history of breast cancer should be monitored especially carefully. In five clinical trials using Depo-Provera CI, the 12-month LifeTable failure rate for the group of women treated with Depo-Provera CI was 0.7 The effectiveness of Depo-Provera CI depends on whether the patient returns for
repeated injections every 3 months (13 weeks). MPA is extensively metabolized in the liver by P450 enzymes. Its metabolism mainly involves reduction of the A ring and/or side chain, loss of the acetyl group, hydroxylation at positions 2, 6, and 21, or a combination of these positions, resulting in 10 to 10 more metabolites.
Calendar calculations are based on the Depo-Provera contraceptive injection. The permanent calendar is produced by Pharmacia and the Upjohn Company. In two clinical trials with Depo-Provera CI, more than 3,900 women treated for up to 7 years reported the following adverse reactions, which may or may not be related to the use of Depo-Provera CI.
Contraception
The study population was between the ages of 15 and 51, of whom 46% were white, 50% nonwhite, and 4.9% of unknown race. Patients received 150 mg of Depo-Provera CI every 3 months (90 days). The median study duration was 13 months with a range of 1 to 84 months.
58 percent of patients remained in the study after 13 months and 34 percent after 24 months. In the risk/benefit analysis of using Depo-Provera CI, women with risk factors for osteoporosis should consider other methods of birth control.
 Source: www.motilaloswal.com
Source: www.motilaloswal.com
Depo-Provera CI may pose an additional risk to patients with risk factors for osteoporosis (eg, metabolic bone disease, chronic alcohol and/or tobacco use, anorexia nervosa, strong history of osteoporosis, or such medications). chronic use that can reduce bone mass (such as anticonvulsants or corticosteroids).
As women continue to use Depo-Provera CI, they experience much less irregular bleeding and more amenorrhea. In clinical trials of Depo-Provera CI, amenorrhea was reported in 55% of women at 12 months, and amenorrhea was reported in 68% of women taking Depo-Provera CI at 24 months.
Bone Fracture Incidence In Women Treated With Depo-Provera Ci
Published SEER-18 2011 incidence rates (corresponding to 2000 US standard population ages) of breast cancer in US women, all races, aged 20–49 years, double breast cancer incidence in women. Those using Depo-Provera CI range from about 72 to about 144 cases per 100,000 women.
To ensure that the patient does not become pregnant at the time of the first injection, the first injection should only be given during the first 5 days of a normal menstrual cycle. Only in the first 5 days after childbirth, if not breastfed;
And if only breast milk is given, then only in the sixth postpartum week. If the time interval between injections is longer than 13 weeks, the doctor must determine whether the patient is pregnant before administering the medicine.
The effectiveness of Depo-Provera CI depends on adherence to the dosing schedule. A retrospective study of 312,395 women using contraception was conducted in the United Kingdom to examine the relationship between Depo-Provera CI injection and the incidence of bone fractures.
Return Of Fertility
Fracture rates were compared between Depo-Provera CI users and contraceptive users who had no record of Depo-Provera CI use. The incidence rate ratio
(IRR) for any fracture during the follow-up period (median = 5.5 years) was 1.41 (95% CI 1.35, 1.47).
It is not known whether this is related to the use of Depo-Provera CI or other related lifestyle factors that affect fracture rates. A study was conducted to evaluate the prevention of BMD loss in adolescents with Depo-Provera CI.
After discontinuation of Depo-Provera CI in these adolescents, mean total hip and femur BMD 5 years (60 months) after treatment in the subgroup of adolescents treated for more than 2 years. The lesion did not heal completely [see Clinical Studies.
14.3)]. Similarly, in adults, mean BMD at the hip, femur, and lumbar spine showed only partial recovery up to 2 years after treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Longer treatment duration and smoking were associated with less BMD recovery after the last DepoProvera CI injection.
Weight Gain
Table 6 shows the extent of recovery in BMD up to 60 months after treatment in adolescents who received DepoProvera CI for two years or less compared with more than two years. Post-treatment follow-up showed that in women treated for more than two years, only spine BMD returned to baseline after treatment was stopped.
Adolescents treated with Depo-Provera CI for more than two years did not return to baseline BMD at the femoral neck and hip 60 months after treatment. Untreated adolescents gained BMD during the trial period (data not shown) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
 Source: mnk.pl
Source: mnk.pl
After stopping Depo-Provera CI, ovulation and return to fertility may be delayed. In a large US study of women who stopped using Depo-Provera CI to become pregnant, data were available for 61% of them. Of the 188 women who stopped the study to become pregnant, 114 became pregnant.
Based on life table analysis of these data, 68% of women who become pregnant are expected to conceive within 12 months, 83% within 15 months, and 93% after the last injection. Can get pregnant within 18 months.
Switching From Other Methods Of Contraception
months. For those who did become pregnant, the median time to conception ranged from 4 to 31 months after the last injection and was not related to duration of use. Data were not available for the 39% of patients who discontinued Depo-Provera CI to become pregnant and who were lost to follow-up or changed their minds.
Read this patient information carefully before deciding whether Depo-Provera CI is right for you. This information is not a substitute for talking to your gynecologist or other health care provider who specializes in women’s health. If you have any questions about Depo-Provera CI, ask your healthcare provider.
You should also learn about other birth control methods in order to choose the method that is right for you. HIV protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: significant changes (increases or decreases) in progestin levels have been observed in some cases of concomitant use of HIV protease inhibitors.
In some cases, significant changes (increase or decrease) in progestin levels have been reported when used in combination with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. The most common adverse reactions (incidence >5%) are: menstrual disturbances (bleeding or spotting) 57% at 12 months, 32% at 24 months, abdominal pain/discomfort 11%, weight gain >10 pounds 38% at 24 months
Bone Mineral Density Changes In Adolescent Females To Years Of Age Treated With Depo-Provera Ci
, dizziness 6%, headache 17%, nervousness 11%, decreased libido 6%. (6.1) Women tend to gain weight during Depo-Provera CI therapy. From a baseline mean body weight of 136 pounds, women who completed 1 year of DepoProvera CI gained an average of 5.4 pounds.
Women who completed 2 years of therapy gained an average of 8.1 pounds. Average 13.8 lbs. By age 6, women gained an average of 16.5 pounds. In a study that calculated the total exposure to Depo-Provera CI, the fracture rate was higher in users who received fewer than 8 injections than in women who received 8 or more injections.
However, it is unclear whether cumulative exposure, which may include periods of intermittent use separated by periods of non-use, is a more useful measure of risk than exposure measures based on continuous use. Accounting Open all.
Biology Brochures & Catalogs Business Education CBSE Chemistry Competitive Exam Computer Dictionary Economics Education English Essay Exam Question Paper General Gita Press Goswami Tulsidas Hanuman Prasad Kanya Lal Munshi Legal Forms PDF List Lord Hanuman Lord Shiva Maharshi Vaidyas Map Collection NCERT Textbook & Solutions Politdf Science Premchand
Loss Of Bone Mineral Density
product price list project report Ram Sharma Acharya science Shankaracharya sociology national liquor price lists Stock market Stotram Swami Vivekananda template and letter samples UPSC free materials UPSC syllabus Valmiki culture Recommended for more than 2 years because of long term treatment effect of Depo-Provera CI
on bone mineral density (BMD) is not used (unless other methods of birth control are considered inadequate) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Doses do not need to be adjusted according to body weight [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
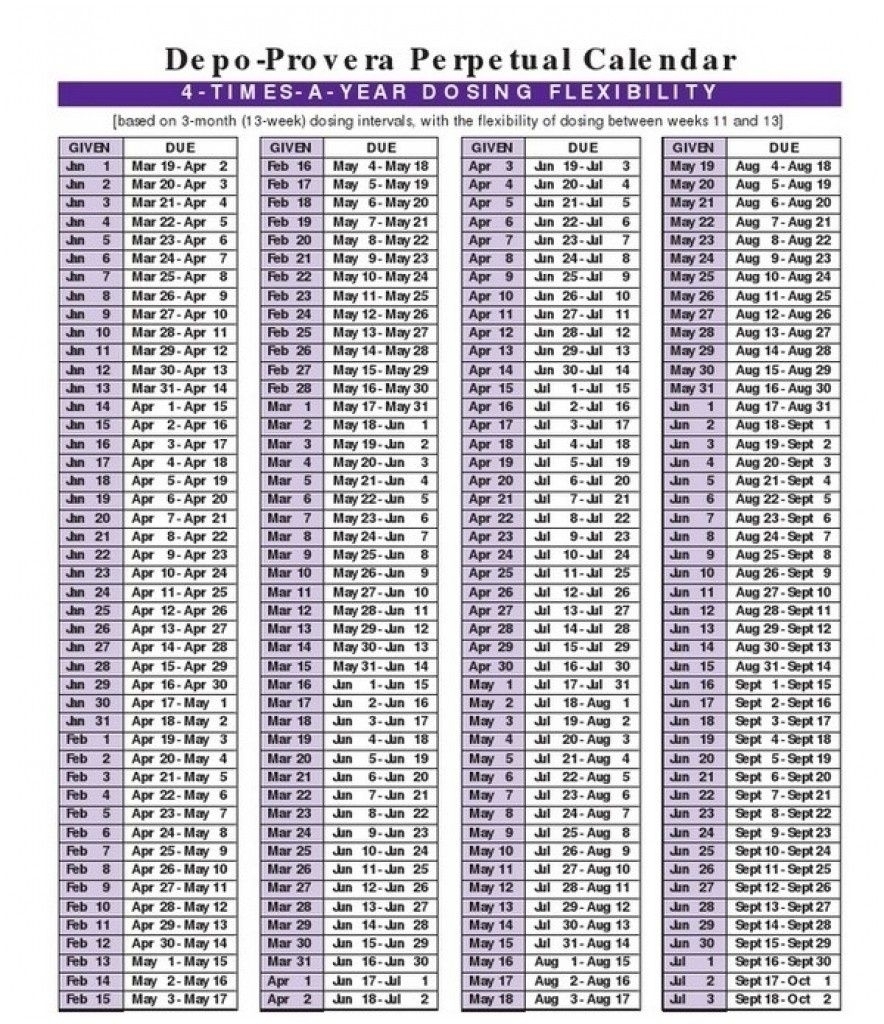 Source: calendarinspiration.com
Source: calendarinspiration.com
The recommended dose is 150 mg of Depo-Provera CI every 3 months (13 weeks) by deep intramuscular (IM) injection into the gluteal muscle or deltoid muscle using strict aseptic technique, alternating sites with each injection. As with any IM injection, to avoid inadvertent subcutaneous injection, body acclimatization should be assessed prior to each injection to determine whether a longer needle is specifically required for gluteal IM injection.
It is not known whether use of Depo-Provera CI during adolescence or early adulthood, a critical period of bone growth, will reduce peak bone mass and increase the risk of osteoporotic fractures later in life [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Injection Site Reactions
Sometimes drugs are prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in the patient’s instructions for use. This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Depo-
Provera CI. If you would like more information, contact your healthcare provider.
You can ask your healthcare provider for information about Depo-Provera CI that is written for healthcare providers. When switching from other contraceptive methods, Depo-Provera CI should be administered in such a way as to provide continuous contraceptive coverage based on the mechanism of action of both methods (eg, with oral contraceptives).
Provera CI the day after the last active pill or the day after the last, last inactive pill). A statistically nonsignificant increase in the RR estimate for invasive squamous cell cervical cancer was associated with the use of Depo-Provera CI in women with first onset before age 35 (RR 1.22 to 1.28 and 95% CI 0.93 to 1.70).
The nonsignificant overall relative rate for invasive squamous cell cervical cancer in women using Depo-Provera was 1.11 (95% CI 0.96 to 1.29), CI. There was no trend in risk with respect to duration of use or time since initial or last exposure.
Clinical Trials Experience
Depo-Provera CI contains medroxyprogesterone acetate, a progesterone derivative, as the active ingredient. Medroxyprogesterone acetate is active parenterally and orally. It is white or off-white. Odorless crystalline powder, stable in air and melting between 200°C and 210°C.
It is well soluble in chloroform, soluble in acetone and dioxin, slightly soluble in alcohol and methanol, slightly soluble in ether and insoluble in water. Depo-Provera Perpetual Calendar PDF Quick Download Link is provided below this article.
You can view PDF demo, PDF size, page number and direct free PDF download of ‘Depo-Provera Perpetual Schedule Calendar’ by using download button. Overall, there were very few osteoporotic fractures (fracture sites associated with low BMD) in the study, and the incidence of osteoporotic fractures was not higher in Depo-Provera CI users than in non-users.
Importantly, this study could not determine whether use of Depo-Provera CI affected fracture rates later in life. The effects of using Depo-Provera CI (150 mg) for up to 240 weeks (4.6 years) were evaluated in an open-label, non-randomized clinical trial in 389 adolescent females (aged 12 to 18 years).
Bone Mineral Density Changes In Women Treated With Depo-Provera Ci
Use of Depo-Provera CI was associated with a significant reduction in BMD from baseline.
printable depo provera perpetual calendar, depo shot calendar, depo provera calendar printable pdf, depo printable calendar, depo provera perpetual calendar pdf, depo calendar october, depo shot calendar 2022, depo provera injection calendar pdf

