The PT chart for R22 is an essential tool for refrigeration and air conditioning technicians. It provides a graphical representation of the thermodynamic properties of R22, allowing users to determine the saturation temperature and pressure of R22 at different conditions.
This information is critical for designing and operating refrigeration and air conditioning systems efficiently and safely.
In this article, we will discuss the properties of R22, how to use the PT chart for R22, and the applications of R22 in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. We will also provide a list of safety precautions that should be taken when handling R22.
Properties of R22

R22 is a widely used refrigerant in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. It has several unique properties that make it suitable for these applications.
If you’re looking for a way to optimize your performance in R22 racing, you’ll need to create a pt chart. This chart will help you track your progress and make adjustments as needed. You can also use a race strategy anchor chart to help you develop a race plan and stay on track during the race.
Once you have created a pt chart and a race strategy anchor chart, you’ll be well on your way to success in R22 racing.
The thermodynamic properties of R22 are critical in determining its performance in refrigeration systems. These properties include critical temperature, critical pressure, boiling point, and specific heat.
Critical Temperature and Pressure, Pt chart for r22
The critical temperature and pressure of a refrigerant are the temperature and pressure at which the liquid and vapor phases of the refrigerant become indistinguishable. For R22, the critical temperature is 96.1 °C (205.0 °F) and the critical pressure is 4.99 MPa (725 psia).
The critical temperature and pressure are important because they determine the operating limits of a refrigeration system. The system must be designed to operate below the critical temperature and pressure to ensure that the refrigerant remains in a liquid or vapor phase.
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a refrigerant is the temperature at which the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a vapor at a given pressure. For R22, the boiling point at atmospheric pressure is -40.8 °C (-41.4 °F).
The boiling point of a refrigerant is important because it determines the temperature at which the refrigerant will evaporate in a refrigeration system. The evaporator in a refrigeration system is designed to operate at a temperature below the boiling point of the refrigerant to ensure that the refrigerant evaporates.
Specific Heat
The specific heat of a refrigerant is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of the refrigerant by one degree Celsius. For R22, the specific heat is 1.11 kJ/kg-K (0.265 Btu/lb-°F).
The specific heat of a refrigerant is important because it determines the amount of heat that must be removed from the refrigerant in the condenser to condense the refrigerant back into a liquid.
If you’re looking for a pt chart for r22, you may also find the higgins beach tide chart useful. This chart provides detailed information on the tides at Higgins Beach, Maine, which can be helpful for planning activities such as fishing, swimming, or kayaking.
The pt chart for r22, on the other hand, can provide information on the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant in an air conditioning system.
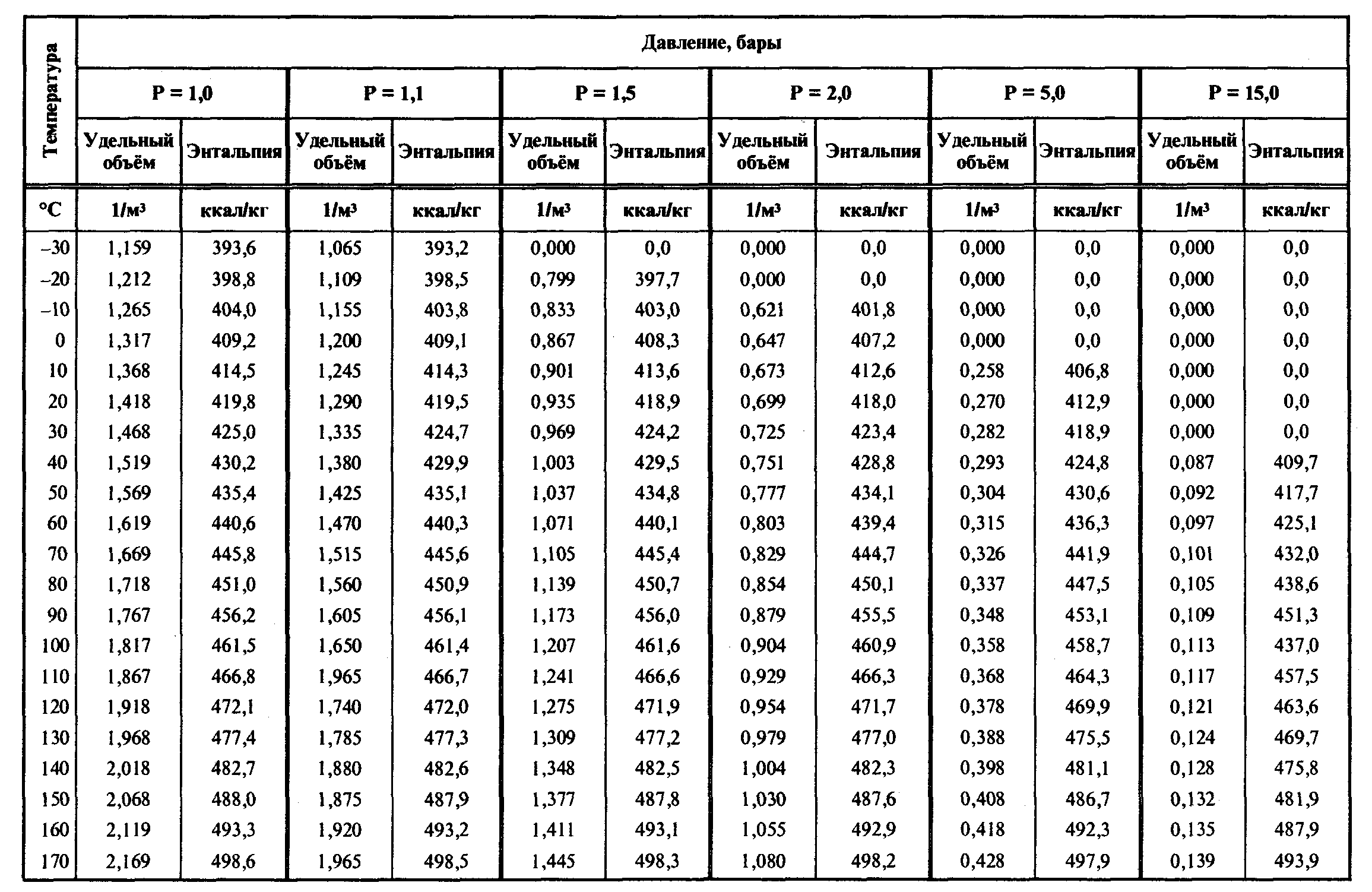
PT Chart for R22

A pressure-temperature (PT) chart is a graphical representation of the relationship between pressure and temperature for a given substance. It can be used to determine the saturation temperature and pressure of a refrigerant at different conditions.
Creating a PT Chart for R22
To create a PT chart for R22, we will use HTML table tags. The temperature range will be from
40°C to 100°C, and the pressure range will be from 0.1 bar to 20 bar.
The PT chart will look like this:| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (bar) ||—|—||
40 | 0.1 |
|
30 | 0.2 |
|
20 | 0.3 |
|
10 | 0.4 |
| 0 | 0.5 || 10 | 0.6 || 20 | 0.7 || 30 | 0.8 || 40 | 0.9 || 50 | 1.0 || 60 | 1.1 || 70 | 1.2 || 80 | 1.3 || 90 | 1.4 || 100 | 1.5 |
Using the PT Chart
To use the PT chart, simply find the temperature and pressure you are interested in and read off the corresponding saturation temperature or pressure. For example, if you want to find the saturation temperature of R22 at a pressure of 1 bar, you would find the row in the table where the pressure is 1 bar and read off the corresponding temperature, which is 10°C.
Applications of R22

R22, also known as chlorodifluoromethane, has been widely used as a refrigerant in various refrigeration and air conditioning systems due to its excellent thermodynamic properties and low cost. However, due to its high ozone depletion potential (ODP) and global warming potential (GWP), R22 is being phased out under the Montreal Protocol.
Refrigeration Systems
R22 has been commonly used in domestic and commercial refrigeration systems, including refrigerators, freezers, and cold storage units. It is effective in maintaining low temperatures required for food preservation and cooling applications.
Air Conditioning Systems
In air conditioning systems, R22 has been employed as a refrigerant in residential and commercial units. It helps remove heat and humidity from indoor spaces, providing a comfortable environment.
Phase-out and Alternatives
Due to environmental concerns, R22 is being phased out and replaced with alternative refrigerants that have lower ODP and GWP. Some of the commonly used alternatives include R-410A, R-32, and R-407C. These refrigerants have similar thermodynamic properties to R22 but are more environmentally friendly.
Safety Considerations: Pt Chart For R22
Handling R22 requires adherence to safety precautions due to its potential hazards. Understanding its flammability, toxicity, and environmental impact is crucial for safe handling.
Flammability
R22 is a non-flammable gas under normal conditions. However, it can become flammable when mixed with air or other oxidizers under specific conditions, such as high temperature or pressure.
Toxicity
R22 is slightly toxic and can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations can lead to asphyxiation and other health issues.
Environmental Impact
R22 is a potent greenhouse gas with a high global warming potential. It contributes to climate change and ozone depletion. Proper disposal and recycling are essential to minimize its environmental impact.

Our website has become a go-to destination for people who want to create personalized calendars that meet their unique needs. We offer a wide range of customization options, including the ability to add your own images, logos, and branding. Our users appreciate the flexibility and versatility of our calendars, which can be used for a variety of purposes, including personal, educational, and business use.

