Welcome to the world of welding lead size charts! In this guide, we’ll dive into the depths of lead sizes, amperage ratings, and everything else you need to know to choose the perfect leads for your welding adventures.
Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, understanding lead size is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and the quality of your welds. So, let’s get started!
Welding Lead Sizes

Welding lead sizes are an important consideration for any welder. The size of the lead will determine how much amperage it can handle, which in turn will affect the thickness of the metal that can be welded.
Relationship between Lead Size and Amperage Capacity
The relationship between lead size and amperage capacity is linear. This means that as the lead size increases, the amperage capacity also increases. The following table shows the different welding lead sizes and their corresponding amperage ratings:| Lead Size | Amperage Rating ||—|—|| 10 AWG | 25 amps || 8 AWG | 40 amps || 6 AWG | 60 amps || 4 AWG | 80 amps || 2 AWG | 100 amps |
Choosing the Correct Lead Size
The correct lead size for a specific welding application will depend on the thickness of the metal that is being welded. The following table provides a general guide to choosing the correct lead size:| Metal Thickness | Lead Size ||—|—|| Up to 1/8 inch | 10 AWG || 1/8 inch to 1/4 inch | 8 AWG || 1/4 inch to 1/2 inch | 6 AWG || 1/2 inch to 1 inch | 4 AWG || Over 1 inch | 2 AWG |It is important to note that these are just general guidelines.
The actual lead size that is required will depend on the specific welding application.
Lead Size Chart

The lead size chart provides essential information for selecting the appropriate welding lead size for a given application. It includes crucial parameters such as amperage rating, voltage drop per foot, resistance per foot, and weight per foot, helping ensure safe and efficient welding operations.
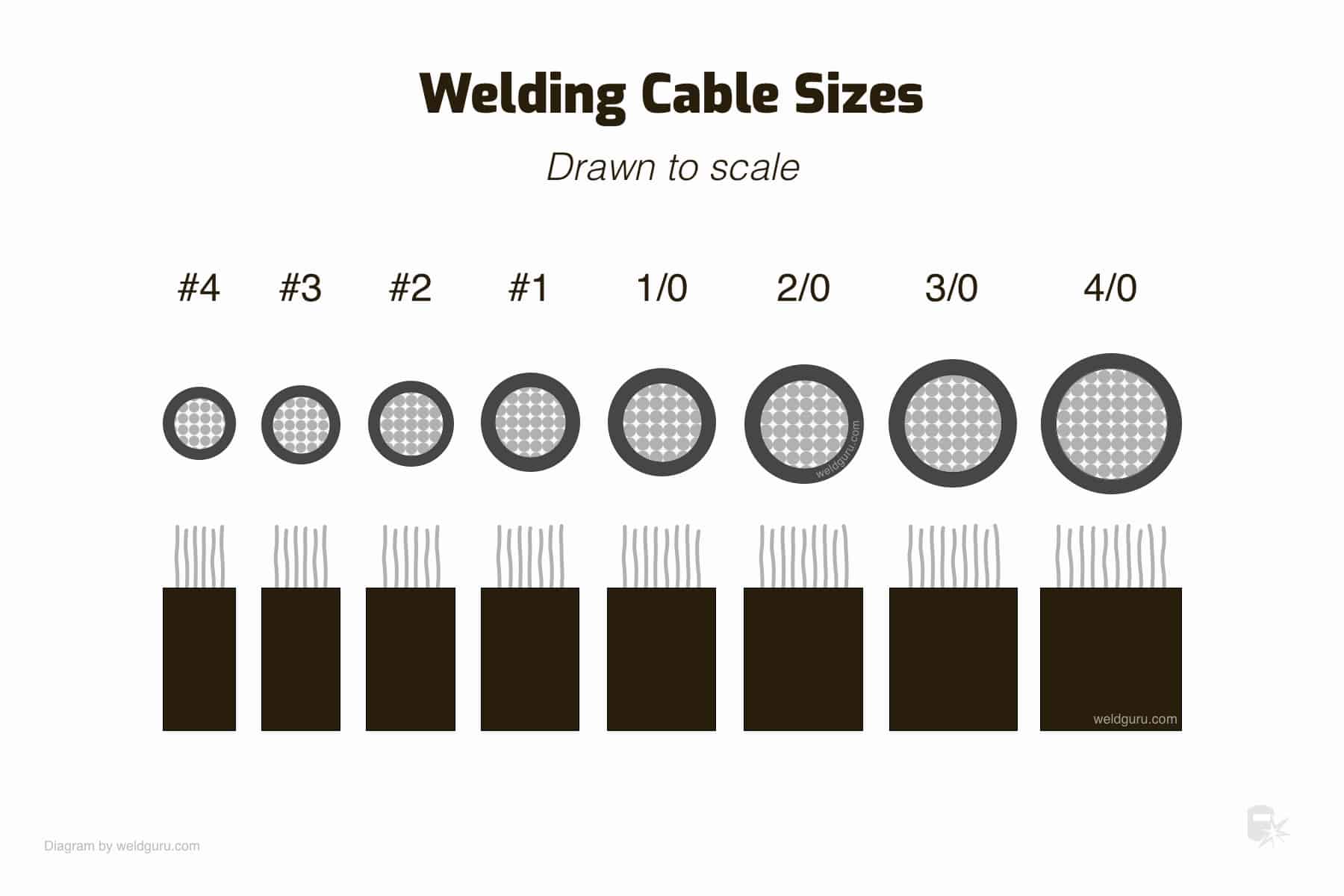
To determine the correct welding lead size for your project, consult a welding lead size chart. These charts provide guidelines based on the amperage of your welder and the length of the lead. For instance, a 200-amp welder with a 50-foot lead would require a 2/0 AWG cable.
Similarly, you can find the optimal lead size for any welding setup. While you’re exploring welding resources, don’t forget to check out the elvis presley natal chart for insights into the King of Rock and Roll’s astrological influences. Returning to welding lead size charts, remember that they are essential tools for ensuring safe and efficient welding operations.
Consider the following factors when choosing the lead size:
- Amperage rating:Indicates the maximum current the lead can safely carry.
- Voltage drop per foot:The voltage lost over a given length of lead due to its resistance.
- Resistance per foot:The resistance of the lead per foot of length.
- Weight per foot:The weight of the lead per foot of length, which affects handling and flexibility.
Lead Size Chart
| Lead Size (AWG) | Amperage Rating | Voltage Drop per Foot (V/ft) | Resistance per Foot (Ω/ft) | Weight per Foot (lb/ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/0 | 200 | 0.0045 | 0.0026 | 0.322 |
| 2/0 | 250 | 0.0035 | 0.0018 | 0.403 |
| 3/0 | 300 | 0.0029 | 0.0014 | 0.496 |
| 4/0 | 350 | 0.0024 | 0.0011 | 0.630 |
| 250 MCM | 400 | 0.0020 | 0.0009 | 0.778 |
| 300 MCM | 450 | 0.0018 | 0.0008 | 0.938 |
| 350 MCM | 500 | 0.0016 | 0.0007 | 1.111 |
| 400 MCM | 550 | 0.0015 | 0.0006 | 1.297 |
| 500 MCM | 600 | 0.0013 | 0.0005 | 1.609 |
| 600 MCM | 700 | 0.0011 | 0.0004 | 1.984 |
Factors Affecting Lead Size: Welding Lead Size Chart

The size of welding leads is crucial for ensuring efficient and safe welding operations. Several factors influence the appropriate lead size, including:
Welding Process
Different welding processes demand varying lead sizes. For instance, high-current processes like arc welding require larger leads than low-current processes such as TIG welding.
Welding Current
The amperage of the welding current directly affects the lead size. Higher welding currents necessitate larger leads to handle the increased electrical load.
For welding enthusiasts seeking guidance on lead size, a comprehensive chart is readily available online. Similarly, if you’re planning a captivating evening at the Capitol Theater in Port Chester, a detailed seating chart ( capitol theater port chester seating chart ) will help you secure the best seats.
Returning to the realm of welding, remember to consult the lead size chart for optimal results.
Welding Distance
The distance between the power source and the welding area impacts lead size. Longer distances require larger leads to minimize voltage drop and ensure adequate power delivery.
Ambient Temperature
Ambient temperature plays a role in lead size selection. In hot environments, larger leads are preferred to dissipate heat effectively and prevent overheating.
Lead Length and Voltage Drop

The length of the welding lead can significantly impact the voltage drop experienced in the welding circuit. As the lead length increases, the resistance of the lead also increases, leading to a higher voltage drop. This voltage drop can reduce the welding power available at the arc, resulting in reduced weld quality and productivity.
Voltage Drop Table
The following table provides the approximate voltage drop per foot for different lead sizes and lengths:
| Lead Size (AWG) | Voltage Drop per Foot (mV/ft) |
|---|---|
| 12 | 1.3 |
| 10 | 0.8 |
| 8 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 0.2 |
Importance of Minimizing Voltage Drop
Minimizing voltage drop in welding applications is crucial for maintaining optimal weld quality and productivity. Excessive voltage drop can lead to the following issues:
- Reduced arc stability and spatter
- Decreased weld penetration and fusion
- Increased porosity and weld defects
- Reduced welding speed and efficiency
Therefore, it is essential to use welding leads of appropriate size and length to minimize voltage drop and ensure optimal welding performance.
Lead Care and Maintenance

Welding leads are essential components of any welding system, and proper care and maintenance are crucial to ensure their longevity and safety. Regular inspections, cleaning, and repairs can extend the life of welding leads and prevent accidents.
Lead Inspection, Welding lead size chart
Regularly inspect welding leads for any signs of damage or wear. Look for:
- Cuts or abrasions in the insulation
- Exposed wires
- Loose or damaged connectors
- Kinks or bends in the lead
Damaged leads can pose a safety hazard and should be repaired or replaced immediately.
Lead Repair and Replacement
If a welding lead is damaged, it is important to repair or replace it as soon as possible. Minor damage, such as small cuts or abrasions in the insulation, can be repaired using electrical tape. However, more severe damage, such as exposed wires or loose connectors, requires professional repair or replacement.
When replacing a welding lead, it is important to use a lead of the same gauge and length as the original. Using a lead of a different gauge or length can affect the welding performance and safety.

.gallery-container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 10px;
justify-content: center;
}
.gallery-item {
flex: 0 1 calc(33.33% – 10px); /* Fleksibilitas untuk setiap item galeri */
overflow: hidden; /* Pastikan gambar tidak melebihi batas kotak */
position: relative;
margin-bottom: 20px; /* Margin bawah untuk deskripsi */
}
.gallery-item img {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
object-fit: cover; /* Gambar akan menutupi area sepenuhnya */
object-position: center; /* Pusatkan gambar */
}
.image-description {
text-align: center; /* Rata tengah deskripsi */
}
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-item {
flex: 1 1 100%; /* Full width di layar lebih kecil dari 768px */
}
}

Our website has become a go-to destination for people who want to create personalized calendars that meet their unique needs. We offer a wide range of customization options, including the ability to add your own images, logos, and branding. Our users appreciate the flexibility and versatility of our calendars, which can be used for a variety of purposes, including personal, educational, and business use.

