Dr boz ratio chart – Step into the realm of liver health as we delve into the depths of the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart, a diagnostic tool that unravels the secrets of liver function. This comprehensive guide will empower you with the knowledge to interpret this chart effectively, enabling you to make informed decisions about your liver health.
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is a valuable instrument in assessing liver function, providing insights into a range of liver conditions. By examining the delicate balance of bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and gamma-glutamyl transferase, this chart unveils a wealth of information about your liver’s well-being.
Definition and Significance of the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart: Dr Boz Ratio Chart
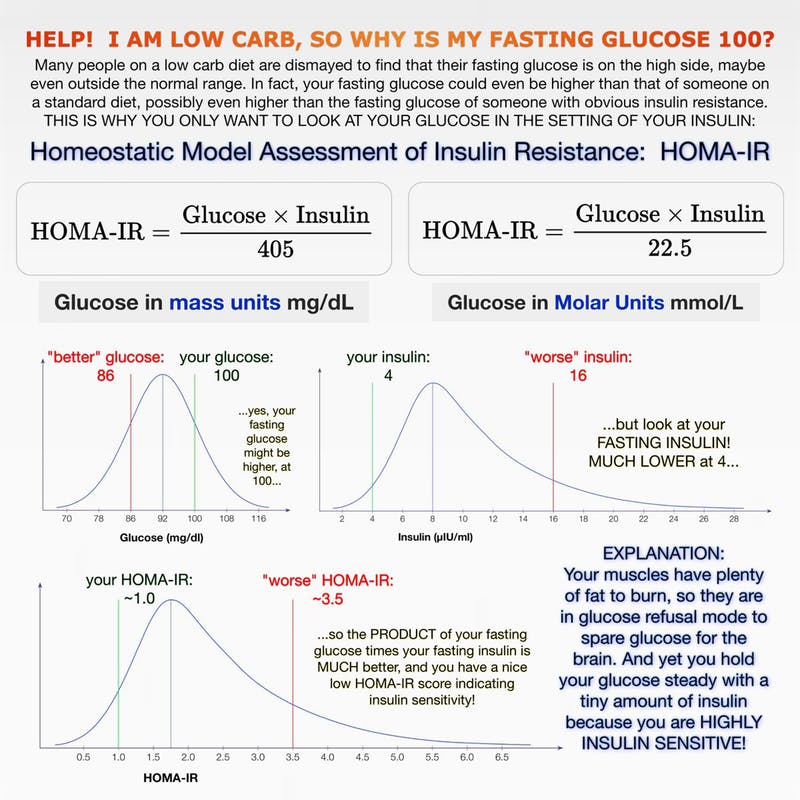
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is a valuable tool for healthcare professionals to assess liver function and detect potential liver damage. It is a simple and non-invasive method that uses a combination of blood tests to calculate a ratio that can indicate the health of the liver.The
Dr. Boz Ratio is calculated using the following formula:“`Dr. Boz Ratio = (Alkaline Phosphatase / Alanine Aminotransferase) x 100“`Normal Dr. Boz Ratio values typically range from 0.6 to 1.5. Higher ratios may indicate liver damage or dysfunction.
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is a tool used to assess the overall balance of a person’s astrological chart. It can be used to identify areas of strength and weakness, and to provide guidance on how to improve one’s life.
For example, Natalie Portman’s birth chart shows that she has a strong emphasis on the element of fire, which gives her a passionate and driven nature. However, she also has a significant amount of air in her chart, which can make her prone to anxiety and overthinking.
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart can help her to understand how to balance these different elements in her life.
Components of the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart
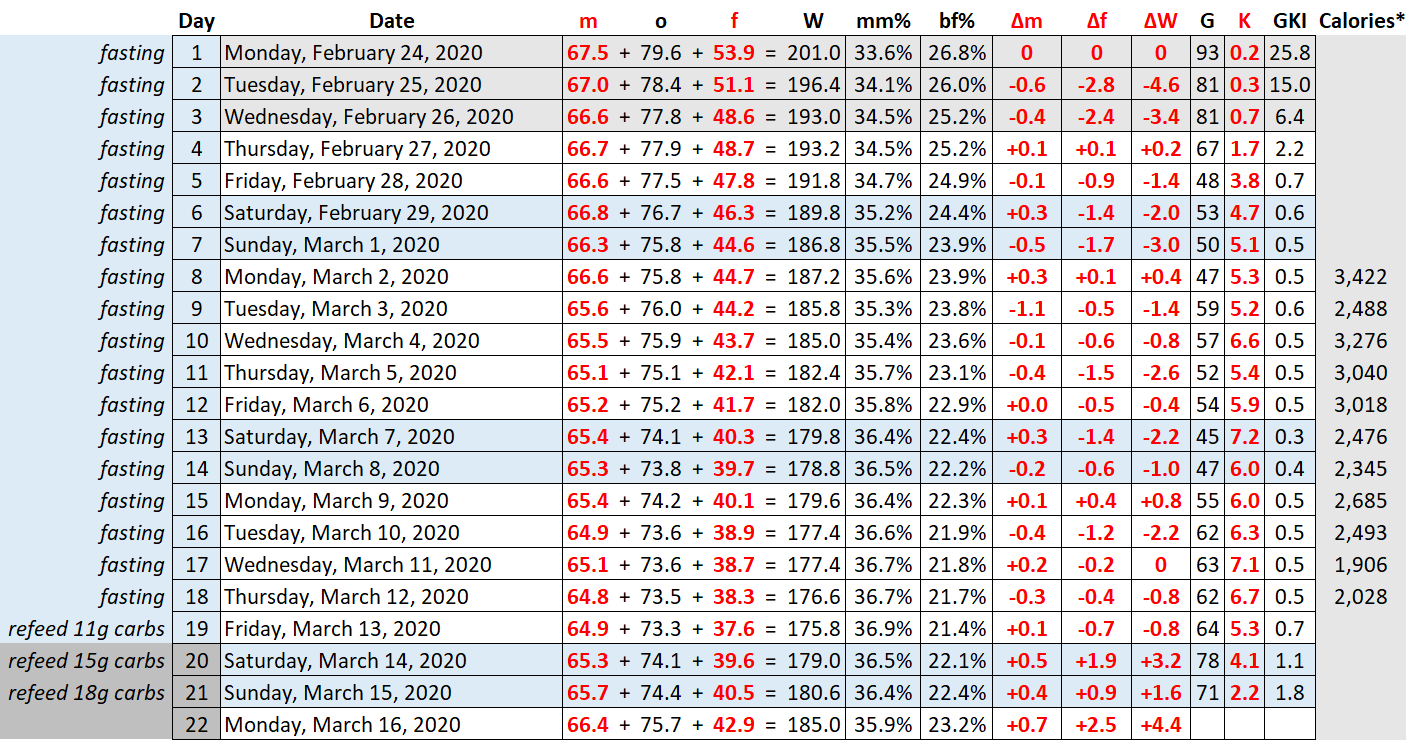
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is a diagnostic tool that utilizes four key laboratory values to assess liver function and identify potential underlying liver diseases. These components are:
- Direct Bilirubin:Represents the conjugated form of bilirubin, which is water-soluble and can be excreted by the kidneys. Elevated levels of direct bilirubin indicate cholestasis, a condition where bile flow is obstructed.
- Total Bilirubin:Encompasses both direct and indirect bilirubin. Elevated total bilirubin levels can indicate increased bilirubin production (hemolysis) or impaired bilirubin clearance (liver disease or cholestasis).
- Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP):An enzyme found in the liver, bones, and intestines. Elevated ALP levels can indicate cholestasis, bone disease, or liver damage.
- Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT):An enzyme found in the liver, pancreas, and kidneys. Elevated GGT levels can indicate liver damage, alcohol abuse, or certain medications.
Interpretation of the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart

Interpreting the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart involves understanding the relationship between the ratios and the underlying liver conditions. The ratio provides valuable insights into the health of the liver and can indicate various liver abnormalities.
Normal Dr. Boz Ratio Range
A normal Dr. Boz Ratio typically falls within the range of 0.8 to 1.2. This range indicates that the liver is functioning normally and there are no significant underlying liver conditions.
The dr boz ratio chart is a great tool for understanding the relationship between body fat and muscle mass. If you’re looking for a more specific tide chart, check out the higgins beach tide chart . The dr boz ratio chart can help you track your progress over time and make sure you’re on the right track to reaching your fitness goals.
Elevated Dr. Boz Ratio
An elevated Dr. Boz Ratio, typically above 1.2, may indicate the presence of liver disease or damage. The higher the ratio, the more severe the liver condition is likely to be.
- Values between 1.2 and 1.5 may indicate mild liver inflammation or fatty liver disease.
- Values between 1.5 and 2.0 may indicate moderate liver damage, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis.
- Values above 2.0 may indicate severe liver damage or liver failure.
Low Dr. Boz Ratio
A low Dr. Boz Ratio, typically below 0.8, may indicate liver dysfunction or cholestasis. Cholestasis is a condition where bile flow is obstructed, leading to a buildup of bile acids in the liver.
- Values between 0.6 and 0.8 may indicate mild cholestasis.
- Values below 0.6 may indicate severe cholestasis or liver failure.
Limitations and Applications of the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is a useful tool for assessing ventricular function, but it has certain limitations. One limitation is that it is based on a single measurement of the left ventricle, and does not take into account changes in ventricular volume over time.
Another limitation is that it does not provide information about the underlying cause of the ventricular dysfunction.Despite these limitations, the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is a useful tool for assessing ventricular function in a variety of clinical settings. It is particularly useful in settings where a quick and easy assessment of ventricular function is needed, such as in the emergency department or in the intensive care unit.
It can also be used to monitor changes in ventricular function over time, and to assess the response to treatment.The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is not a diagnostic tool, and should not be used to make a definitive diagnosis of ventricular dysfunction.
However, it can be used to identify patients who may need further evaluation for ventricular dysfunction, such as an echocardiogram or a cardiac catheterization.
Applicability in Different Clinical Settings
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is applicable in a variety of clinical settings, including:
- Emergency department
- Intensive care unit
- Cardiology clinic
- Pulmonary clinic
- Internal medicine clinic
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is particularly useful in settings where a quick and easy assessment of ventricular function is needed, such as in the emergency department or in the intensive care unit. It can also be used to monitor changes in ventricular function over time, and to assess the response to treatment.
When the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart May Be Useful as a Diagnostic Tool
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is not a diagnostic tool, and should not be used to make a definitive diagnosis of ventricular dysfunction. However, it can be used to identify patients who may need further evaluation for ventricular dysfunction, such as an echocardiogram or a cardiac catheterization.The
Dr. Boz Ratio Chart may be useful as a diagnostic tool in the following situations:
- When a patient presents with symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or edema.
- When a patient has a history of heart disease, such as a heart attack or coronary artery disease.
- When a patient is taking medications that can cause ventricular dysfunction, such as chemotherapy drugs or certain anti-inflammatory medications.
In these situations, the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart can help to identify patients who may need further evaluation for ventricular dysfunction.
Comparison with Other Liver Function Tests
The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart is a valuable tool for assessing liver function, but it’s essential to understand how it compares to other liver function tests to make informed decisions about patient care.
Here’s a brief comparison of the Dr. Boz Ratio Chart with other commonly used liver function tests:
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
- ALT is an enzyme primarily found in the liver. Elevated ALT levels can indicate liver damage or inflammation.
- ALT is more sensitive than AST in detecting acute liver injury, but it can also be elevated in other conditions, such as muscle damage.
- The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart incorporates ALT as one of its components, making it more comprehensive than ALT alone.
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
- AST is another enzyme found in the liver and other tissues, including the heart and muscles.
- Elevated AST levels can indicate liver damage or inflammation, as well as damage to other organs.
- AST is less sensitive than ALT in detecting acute liver injury, but it may be more specific.
Liver Function Panel (LFT)
- An LFT is a group of tests that evaluate overall liver function.
- It typically includes ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin, and albumin.
- An LFT provides a more comprehensive assessment of liver function than individual tests but may not be as sensitive in detecting specific liver abnormalities.
Illustrative Examples and Case Studies

The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart finds practical applications in various clinical settings, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of liver conditions.
Case Studies, Dr boz ratio chart
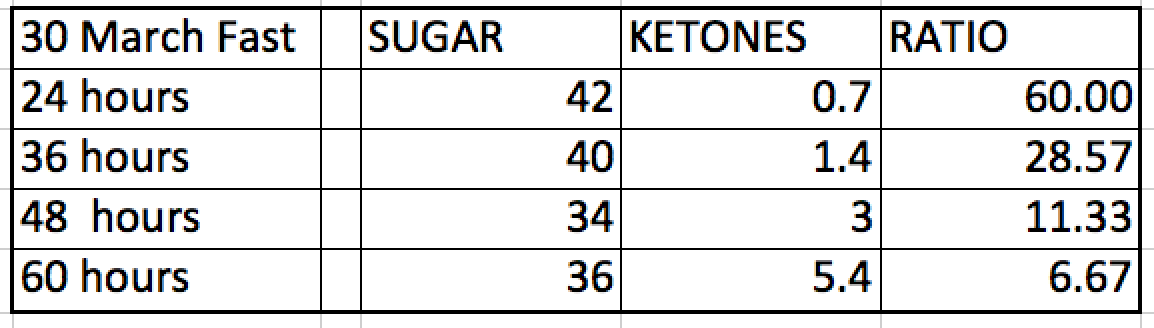
- Case 1:A 55-year-old male with a history of alcohol abuse presented with jaundice and elevated liver enzymes. The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart showed a ratio of 0.6, indicating cholestasis, which was later confirmed by liver biopsy.
- Case 2:A 32-year-old female with autoimmune hepatitis exhibited fatigue, joint pain, and abnormal liver function tests. The Dr. Boz Ratio Chart revealed a ratio of 1.2, suggesting hepatocellular damage, which was consistent with her diagnosis.

.gallery-container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 10px;
justify-content: center;
}
.gallery-item {
flex: 0 1 calc(33.33% – 10px); /* Fleksibilitas untuk setiap item galeri */
overflow: hidden; /* Pastikan gambar tidak melebihi batas kotak */
position: relative;
margin-bottom: 20px; /* Margin bawah untuk deskripsi */
}
.gallery-item img {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
object-fit: cover; /* Gambar akan menutupi area sepenuhnya */
object-position: center; /* Pusatkan gambar */
}
.image-description {
text-align: center; /* Rata tengah deskripsi */
}
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-item {
flex: 1 1 100%; /* Full width di layar lebih kecil dari 768px */
}
}

Our website has become a go-to destination for people who want to create personalized calendars that meet their unique needs. We offer a wide range of customization options, including the ability to add your own images, logos, and branding. Our users appreciate the flexibility and versatility of our calendars, which can be used for a variety of purposes, including personal, educational, and business use.

