Goose egg incubation chart – Step into the captivating world of goose egg incubation with our comprehensive chart, where every detail is meticulously Artikeld to empower you with the knowledge and skills to nurture healthy goslings. From temperature and humidity management to egg turning schedules and troubleshooting tips, this guide serves as your trusted companion throughout the enchanting journey of incubation.
As you delve into the intricacies of goose egg incubation, you’ll discover the optimal conditions for embryo development, the importance of regular egg turning, and the techniques to monitor egg health effectively. Prepare to witness the miracle of life unfold as we guide you through the hatching process, ensuring a successful and rewarding experience.
Goose Egg Incubation Chart Basics
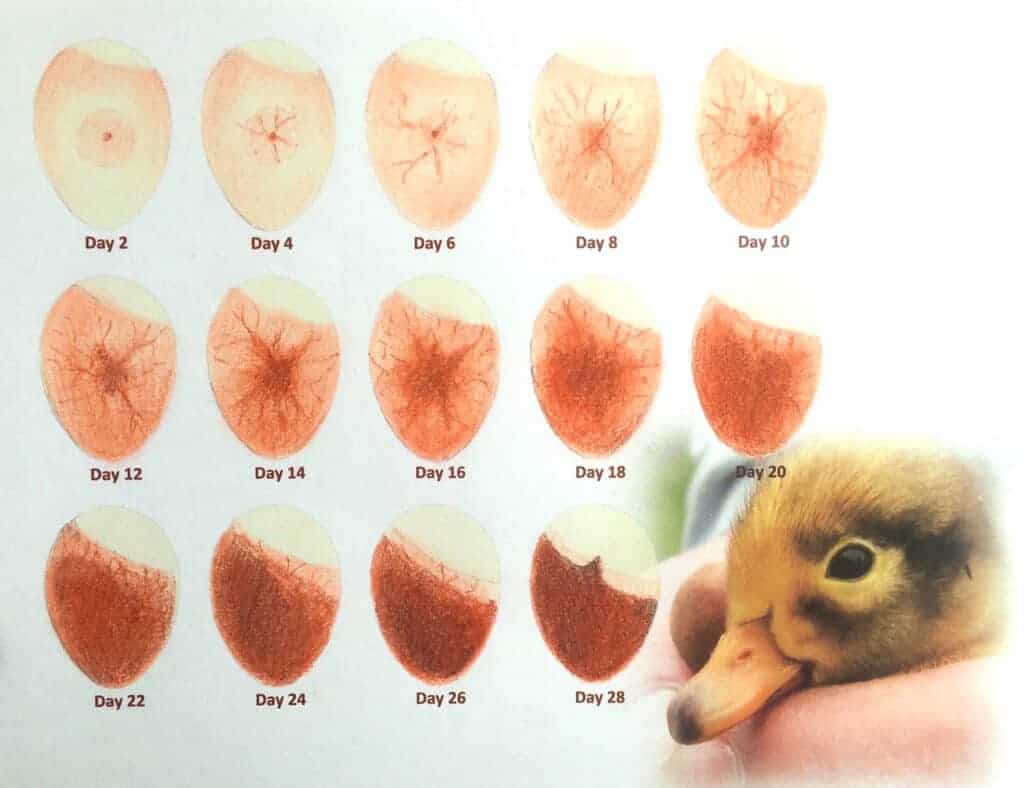
An incubation chart is a valuable tool for successful goose egg hatching. It provides a comprehensive schedule for temperature, humidity, and egg turning, ensuring optimal conditions for embryo development.
The goose egg incubation chart provides a comprehensive guide to hatching goose eggs successfully. Whether you’re a seasoned poultry enthusiast or just starting out, this chart will provide you with valuable insights. For those looking to explore other seating options, the shi stadium seating chart offers a detailed layout of the stadium’s seating arrangements.
Returning to our topic, the goose egg incubation chart also includes tips on egg handling, temperature control, and troubleshooting common problems.
The key parameters tracked in an incubation chart include:
- Temperature:The optimal temperature for goose egg incubation is between 37.5°C (99.5°F) and 38.5°C (101.3°F). Maintaining a consistent temperature is crucial for proper embryo development and hatchability.
- Humidity:The ideal humidity level for goose egg incubation is between 55% and 65%. Proper humidity helps prevent eggs from drying out and promotes the exchange of gases necessary for embryo respiration.
- Egg Turning:Turning goose eggs regularly is essential to prevent the embryo from sticking to the shell and to ensure even distribution of heat. Eggs should be turned at least 4-6 times per day, with the turning angle being at least 45 degrees.
Temperature and Humidity Management

Maintaining proper temperature and humidity levels is crucial for successful goose egg incubation. These factors significantly influence embryo development and can affect hatchability rates.
The optimal temperature for goose egg incubation ranges from 99.5°F (37.5°C) to 100.5°F (38.1°C). During the first 28 days of incubation, a temperature of 100°F (37.8°C)
is ideal. For the remaining 7 days, the temperature can be slightly lowered to 99.5°F (37.5°C).
Humidity levels should be kept at around 55-60% during the first 28 days of incubation. This level helps maintain the moisture content of the eggs and prevents them from drying out. During the last 7 days, humidity can be gradually increased to 65-70% to aid in the hatching process.
Monitoring goose egg incubation requires close attention to temperature and humidity levels. If you’re interested in diving deeper into the world of underwater exploration, you might find the dipsy diver depth chart a valuable resource. Returning to goose egg incubation, it’s essential to maintain optimal conditions throughout the incubation period to ensure healthy gosling development.
Consequences of Temperature and Humidity Fluctuations
- Temperature Fluctuations:Extreme temperature fluctuations can lead to embryo mortality. Temperatures below the optimal range can slow down development, while temperatures above the optimal range can cause dehydration and embryonic abnormalities.
- Humidity Fluctuations:Low humidity levels can cause eggs to lose moisture, leading to decreased hatchability rates. High humidity levels, on the other hand, can promote bacterial growth and embryo death.
Egg Turning Schedule: Goose Egg Incubation Chart
Turning goose eggs regularly during incubation is crucial for the proper development of the embryo. It ensures even heat distribution, prevents the embryo from adhering to the shell, and facilitates gas exchange.
Methods of Egg Turning, Goose egg incubation chart
There are several methods for turning goose eggs:
- Manual turning:This involves manually rotating the eggs by 180 degrees several times a day. It is labor-intensive but provides the most control over the turning process.
- Automatic turning:Automatic incubators come equipped with egg trays that rotate the eggs at regular intervals. This method is convenient and saves time but may not be as precise as manual turning.
- Semi-automatic turning:Some incubators allow for semi-automatic turning, where the user sets the turning interval, and the incubator rotates the eggs automatically.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting

Successful goose egg incubation requires regular monitoring and troubleshooting to ensure optimal conditions for embryo development. Here are some key signs, techniques, and tips to help you monitor and address any issues during the incubation process.
Signs of Healthy and Unhealthy Goose Eggs
During incubation, it’s crucial to observe your goose eggs for signs of health or distress. Healthy eggs will typically exhibit the following characteristics:
- Smooth, unblemished shell
- Firm and slightly elastic when gently squeezed
- Gradually increasing weight over time
- No cracks or leaks
- No foul odor
Unhealthy eggs, on the other hand, may show signs of:
- Dents, cracks, or other shell damage
- Soft or mushy shell
- Decreasing weight over time
- Mold or bacteria growth
- Strong foul odor
Monitoring Egg Development
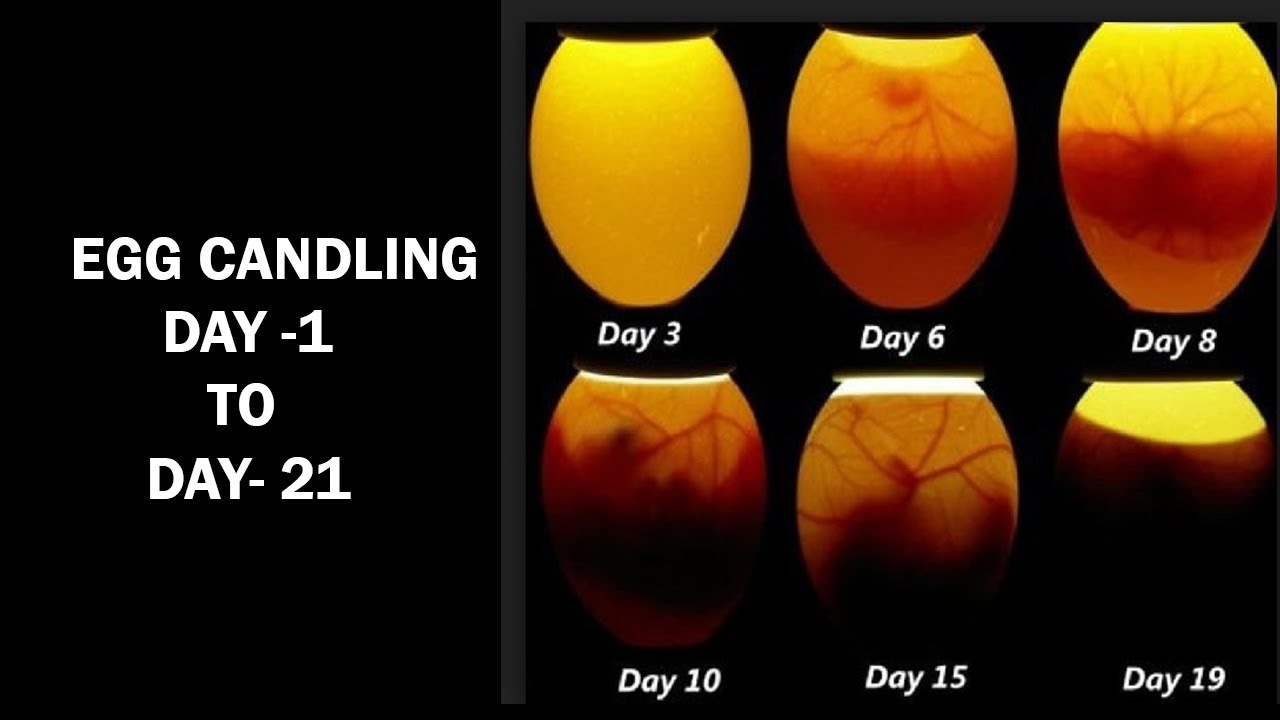
Regular monitoring of egg development is essential to ensure that the embryos are growing and developing properly. Two common techniques used for monitoring are candling and listening for embryo movement.
Candling
Candling involves shining a bright light through the egg to observe the embryo’s development. This technique allows you to check for:
- Embryo movement
- Air cell size and position
- Blood vessels
- Shell integrity
Listening for Embryo Movement
After about 10 days of incubation, you may be able to hear embryo movement by gently tapping the egg against your ear. A strong, rhythmic heartbeat is a positive sign of healthy embryo development.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting Tips
During incubation, you may encounter various problems that can affect embryo development. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
Eggs Not Hatching
- Possible causes:Incorrect incubation temperature, humidity, or egg turning schedule; infertile eggs; embryo mortality
- Troubleshooting tips:Check and adjust incubation conditions; remove infertile eggs; investigate possible causes of embryo mortality
Eggs Pipping but Not Hatching
- Possible causes:Insufficient humidity; embryo weakness or deformities; lack of oxygen
- Troubleshooting tips:Increase humidity; check embryo health and viability; provide adequate ventilation
Embryo Death
- Possible causes:Incorrect incubation conditions; disease or infection; genetic defects
- Troubleshooting tips:Review incubation conditions; consult a veterinarian; select healthy breeding stock
Hatching Process
Goose eggs typically hatch after 28-32 days of incubation. As the hatching date approaches, several signs indicate that the eggs are ready to hatch:
- Pipping:A small hole appears on the eggshell, made by the gosling using its egg tooth.
- Cheeping:The gosling makes faint sounds from inside the egg.
- Egg movement:The egg begins to move as the gosling positions itself for hatching.
Hatching and Care
Hatching can take several hours. Once the gosling emerges, it will be wet and exhausted. Provide a warm, dry place for the gosling to rest and recover. Handle newly hatched goslings gently, as they are fragile.
Within 24 hours of hatching, the goslings should be able to stand and walk. Provide them with access to food and water. Goose starter feed and fresh water should be available at all times.
Factors Affecting Hatching Success
Several factors can affect the hatching success rate of goose eggs:
- Egg quality:Eggs that are cracked, dented, or have thin shells are less likely to hatch successfully.
- Incubation temperature:Maintaining the correct incubation temperature is crucial. Goose eggs should be incubated at 99.5-100.5°F (37.5-38.1°C).
- Humidity:The humidity level in the incubator should be around 55-65%. Too much or too little humidity can affect hatching.
- Egg turning:Goose eggs should be turned regularly during incubation to prevent the embryo from sticking to the shell.
- Disease:Diseases can affect the development of the embryo and reduce hatching success.

Our website has become a go-to destination for people who want to create personalized calendars that meet their unique needs. We offer a wide range of customization options, including the ability to add your own images, logos, and branding. Our users appreciate the flexibility and versatility of our calendars, which can be used for a variety of purposes, including personal, educational, and business use.

