Unveiling the Piston Chart for 410a Refrigerant: A cornerstone of refrigeration systems, the piston chart empowers technicians with a visual representation of refrigerant properties, enabling them to navigate the intricacies of refrigeration cycles with precision and confidence.
Delving into the piston chart’s intricacies, we’ll decipher its axes and scales, unravel the relationship between pressure, temperature, and enthalpy, and master the art of interpreting the saturation curve and superheated vapor region.
Piston Chart for 410a Refrigerant
A piston chart is a graphical representation of the thermodynamic properties of a refrigerant. It is used to determine the state of a refrigerant at a given pressure and temperature. Piston charts are essential for designing and operating refrigeration systems.
The piston chart for 410a refrigerant is a two-dimensional graph that plots pressure on the x-axis and temperature on the y-axis. The chart is divided into regions that represent different states of the refrigerant. The liquid region is located at the bottom of the chart, the vapor region is located at the top of the chart, and the two-phase region is located in between.
Applications of Piston Chart for 410a Refrigerant
Piston charts are used for a variety of applications in refrigeration systems, including:
- Determining the state of a refrigerant at a given pressure and temperature
- Calculating the enthalpy and entropy of a refrigerant
- Designing and optimizing refrigeration systems
- Troubleshooting refrigeration systems
Limitations of Piston Chart for 410a Refrigerant
Piston charts are a valuable tool for designing and operating refrigeration systems, but they have some limitations. Piston charts are only accurate for a specific refrigerant. They cannot be used to determine the state of a refrigerant mixture. Additionally, piston charts do not account for the effects of oil on the refrigerant.
Understanding the Piston Chart
A piston chart is a graphical representation of the thermodynamic properties of a refrigerant. It is a valuable tool for refrigeration technicians and engineers as it allows them to quickly and easily determine the state of a refrigerant at a given pressure and temperature.
Axes and Scales
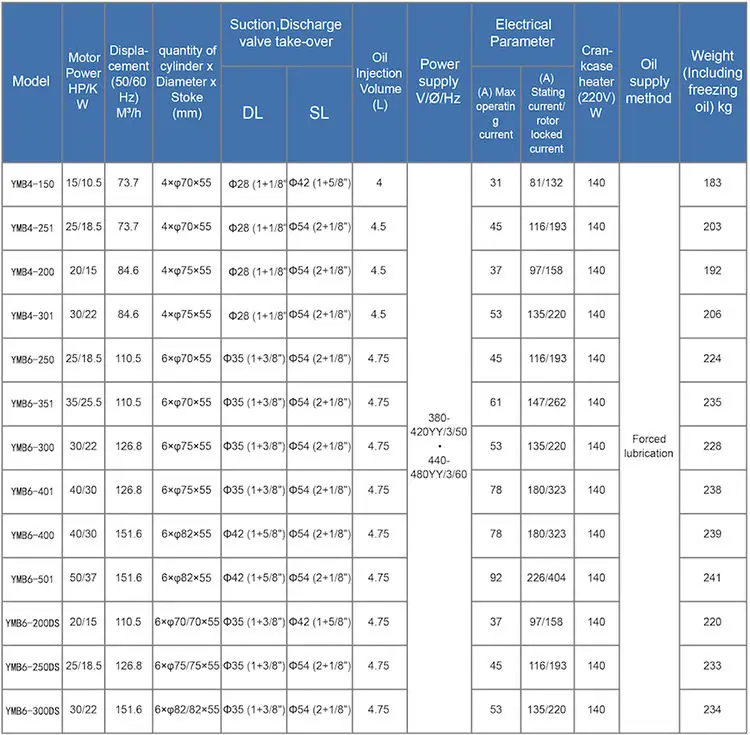
The piston chart for 410a has two axes: the pressure axis and the temperature axis. The pressure axis is typically labeled in pounds per square inch (psi) or bar, while the temperature axis is labeled in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or degrees Celsius (°C).
The scales used on the piston chart are nonlinear. This is because the relationship between pressure, temperature, and enthalpy is not linear. The nonlinearity of the scales can make it difficult to read the chart at first, but with practice, it becomes easier.
Relationship between Pressure, Temperature, and Enthalpy
The piston chart shows the relationship between pressure, temperature, and enthalpy. Enthalpy is a measure of the energy content of a substance. It is typically expressed in British thermal units per pound (Btu/lb) or kilojoules per kilogram (kJ/kg).
On the piston chart, the lines of constant pressure are vertical, while the lines of constant temperature are horizontal. The lines of constant enthalpy are diagonal.
If you’re seeking data on the piston chart for 410a, don’t forget to check out the tide chart for Old Saybrook, CT for additional insights. The piston chart for 410a provides valuable information regarding its operation, while the tide chart can assist you in planning activities influenced by tidal patterns.
Combining these resources offers a comprehensive understanding of both topics.
Saturation Curve and Superheated Vapor Region
The saturation curve on the piston chart is the line that separates the liquid and vapor regions. The saturation curve is also known as the boiling curve. The superheated vapor region is the region above the saturation curve.
The saturation curve shows the pressure and temperature at which a refrigerant will boil. The superheated vapor region shows the pressure and temperature at which a refrigerant is a vapor.
Using the Piston Chart for Calculations: Piston Chart For 410a

The piston chart is a valuable tool for refrigeration technicians and engineers. It allows us to quickly and easily determine refrigerant properties such as pressure, temperature, and enthalpy. We can also use the chart to perform calculations related to refrigeration cycles.
To use the piston chart, we first need to identify the refrigerant we are working with. The chart is divided into sections for different refrigerants. Once we have identified the correct section, we can use the chart to find the properties we need.
Determining Refrigerant Properties
To determine a refrigerant property, we need to know two other properties. For example, if we know the pressure and temperature of a refrigerant, we can use the chart to find the enthalpy.
To find the enthalpy, we first locate the pressure and temperature on the chart. Then, we follow the constant pressure line for the given pressure to the constant temperature line for the given temperature. The point where these two lines intersect is the enthalpy.
Piston charts for 410a provide valuable insights into the performance of refrigeration systems. However, if you’re looking for a different type of chart, you might want to check out the higgins beach tide chart . It’s a great resource for planning your beach activities.
Returning to piston charts, they are an essential tool for any refrigeration technician.
Performing Refrigeration Cycle Calculations
The piston chart can also be used to perform calculations related to refrigeration cycles. For example, we can use the chart to determine the refrigerant mass flow rate, compressor power, and condenser heat rejection.
To perform these calculations, we need to know the refrigerant properties at different points in the refrigeration cycle. We can use the piston chart to find these properties.
Practical Applications
The piston chart is used in a variety of practical applications, including:
- Sizing refrigeration components
- Troubleshooting refrigeration systems
- Designing refrigeration systems
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Piston Chart

A piston chart is a graphical representation of the thermodynamic properties of a refrigerant. It is a useful tool for engineers and technicians who work with refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
There are several advantages to using a piston chart. First, it is a simple and easy-to-use tool. The chart is divided into several sections, each of which represents a different thermodynamic property. This makes it easy to find the information you need quickly and easily.
Second, piston charts are relatively accurate. They are based on experimental data, and they have been shown to be accurate within a few percent.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using a piston chart. First, they are not as accurate as some other methods for determining refrigerant properties. For example, computer software can be used to calculate refrigerant properties with greater accuracy.
Second, piston charts require interpolation. This means that you must estimate the value of a property between two known values. This can lead to errors, especially if the interpolation is not done carefully.
Overall, piston charts are a useful tool for engineers and technicians who work with refrigeration and air conditioning systems. They are simple to use, relatively accurate, and inexpensive. However, they are not as accurate as some other methods for determining refrigerant properties, and they require interpolation.
Comparison with Other Methods
Piston charts are not the only method for determining refrigerant properties. Other methods include:
- Computer software
- Tables
- Equations of state
Computer software is the most accurate method for determining refrigerant properties. However, it can be expensive and time-consuming to use.
Tables are another accurate method for determining refrigerant properties. However, they can be difficult to use, especially if you need to find the value of a property at a specific point.
Equations of state are the most complex method for determining refrigerant properties. However, they are also the most accurate.
The best method for determining refrigerant properties depends on the specific application. If you need the most accurate results, then you should use computer software. If you need a quick and easy method, then you should use a piston chart.
Designing and Creating a Piston Chart for 410a

Designing and creating a piston chart for 410a refrigerant involves several steps. These steps ensure the chart is accurate, informative, and customized for specific applications.
The process typically begins with gathering the necessary data, including pressure, temperature, and enthalpy values for 410a. This data can be obtained from refrigerant tables, software databases, or experimental measurements.
Software and Tools
Once the data is collected, specialized software or tools are used to create the piston chart. These tools provide a graphical interface for plotting the data and generating the chart. Some popular software options include:
- EES (Engineering Equation Solver)
- Refrigerant Properties Calculator (RPC)
- CoolPack
Customization and Optimization, Piston chart for 410a
After creating the basic piston chart, it can be customized and optimized for specific applications. This may involve:
- Adjusting the pressure and temperature ranges to match the operating conditions of the system.
- Adding additional lines or curves to represent different parameters, such as isentropic lines or quality lines.
- Including annotations or labels to enhance the clarity and readability of the chart.
By following these steps and utilizing appropriate software, you can design and create a piston chart for 410a that meets the specific requirements of your application.
Additional Considerations

Using a piston chart effectively requires considering several additional factors that can impact its accuracy and reliability.
Temperature and Pressure Variations
The accuracy of a piston chart depends on the specific temperature and pressure conditions it represents. As temperature and pressure change, the properties of the refrigerant will also change, affecting the chart’s readings.
Using Up-to-Date Refrigerant Data
It is crucial to use up-to-date refrigerant data when creating piston charts. Refrigerant properties can change over time, so using outdated data can lead to inaccurate results.
Maintaining and Updating Piston Charts
Piston charts should be regularly maintained and updated to ensure their accuracy. This includes verifying the data used, checking for any errors, and making necessary adjustments based on the latest refrigerant information.

Our website has become a go-to destination for people who want to create personalized calendars that meet their unique needs. We offer a wide range of customization options, including the ability to add your own images, logos, and branding. Our users appreciate the flexibility and versatility of our calendars, which can be used for a variety of purposes, including personal, educational, and business use.

