Embark on a musical journey with the Trigger Trombone Slide Chart, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the secrets of this extraordinary instrument. Dive into the origins, technicalities, techniques, and maintenance of the trigger trombone, unraveling its captivating sound and versatility.
From its humble beginnings to its modern-day applications, the trigger trombone has evolved as a testament to human ingenuity. Its unique design and innovative trigger mechanism have transformed the trombone landscape, enabling musicians to reach new heights of expression and precision.
Trigger Trombone: Origins and History
The trigger trombone, a distinctive member of the brass instrument family, has a rich and intriguing history that traces back to the early 19th century.
The genesis of the trigger trombone can be attributed to the need for a trombone that could easily and quickly switch between two keys, typically B-flat and F. The initial trigger mechanism was a simple lever that extended the slide, allowing the player to access the lower F key without the need for a separate instrument.
Evolution of the Trigger Mechanism
The trigger mechanism has undergone several iterations since its inception. Early triggers were operated by the player’s left hand, but later designs incorporated a lever that could be actuated by the right hand. This improvement allowed for smoother and more precise key changes during performance.
Timeline of Significant Developments
- 1818:The first known trigger trombone is invented by German instrument maker Heinrich Stölzel.
- 1839:The French trombonist Adolphe Sax patents a trigger trombone with a lever operated by the right hand.
- 1890s:American trombonist Arthur Pryor popularizes the trigger trombone in the United States.
- 20th century:The trigger trombone becomes widely adopted in jazz, big band, and orchestral settings.
Technical Features and Design

The trigger trombone distinguishes itself from other trombones through its unique construction and the incorporation of a trigger mechanism. This mechanism significantly impacts trombone performance, offering enhanced versatility and expressive capabilities.
To master the trigger trombone, it’s essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the slide chart. This chart provides a visual representation of the slide positions and their corresponding pitches. Similarly, in music theory, the dr boz ratio chart is a valuable tool for understanding the relationship between intervals and ratios.
By studying both the trigger trombone slide chart and the dr boz ratio chart, musicians can develop a deeper understanding of their instrument and music theory as a whole.
The trigger trombone’s slide is divided into two sections: the inner and outer slides. The inner slide, which is the shorter of the two, is attached to the bell and moves independently of the outer slide. The outer slide, on the other hand, is connected to the mouthpiece and extends as the player lowers the pitch of the instrument.
Trigger Mechanism
The trigger mechanism is a key component of the trigger trombone. It consists of a lever that, when engaged, allows the player to extend the inner slide independently of the outer slide. This enables the player to quickly and easily switch between different positions, providing greater flexibility in performance.
By engaging the trigger, the player can extend the inner slide by a half step or a whole step, depending on the specific design of the instrument. This allows for rapid and precise pitch adjustments, making the trigger trombone particularly suitable for jazz and other genres that require frequent glissandi and other rapid pitch changes.
Comparison to Other Trombones
Compared to traditional trombones, trigger trombones offer several advantages. The trigger mechanism provides greater flexibility and control over pitch, allowing for a wider range of expressive techniques. Additionally, the trigger trombone’s ability to quickly change positions makes it more suitable for certain musical styles that require rapid pitch changes.
If you’re a brass player looking to master the trigger trombone slide chart, consider using a spac seating chart with seat numbers to visualize the positions. This approach can help you quickly locate the correct slide positions, enabling you to play the instrument with greater accuracy and confidence.
By understanding the spacial relationship between the slide positions, you’ll enhance your overall trombone playing skills.
However, it’s important to note that trigger trombones can be more complex to maintain and repair due to the additional moving parts. They also tend to be more expensive than traditional trombones.
Techniques and Applications: Trigger Trombone Slide Chart

The trigger trombone is played using a combination of traditional trombone techniques and unique techniques made possible by the trigger mechanism. The most common techniques include:
- Triggering:The trigger is used to quickly extend the slide, lowering the pitch by one or more semitones.
- Lip Slurs:Lip slurs are used to smoothly transition between notes, even when the trigger is used.
- Slide Glissandos:Slide glissandos are used to create a smooth, continuous transition between notes, often using the trigger to extend the range of the slide.
Musical Styles
The trigger trombone is used in a wide range of musical styles, including:
- Jazz:The trigger trombone is commonly used in jazz, where it is used for improvisation and soloing.
- Classical:The trigger trombone is also used in classical music, where it is used for orchestral and chamber music.
- Pop and Rock:The trigger trombone is sometimes used in pop and rock music, where it is used for adding a unique sound to the music.
Notable Musicians
Many notable musicians have mastered the trigger trombone, including:
- J.J. Johnson:Johnson was one of the first jazz musicians to use the trigger trombone, and he is considered one of the greatest jazz trombonists of all time.
- Kai Winding:Winding was a jazz trombonist who was known for his use of the trigger trombone in bebop and cool jazz.
- Frank Rosolino:Rosolino was a jazz trombonist who was known for his use of the trigger trombone in West Coast jazz.
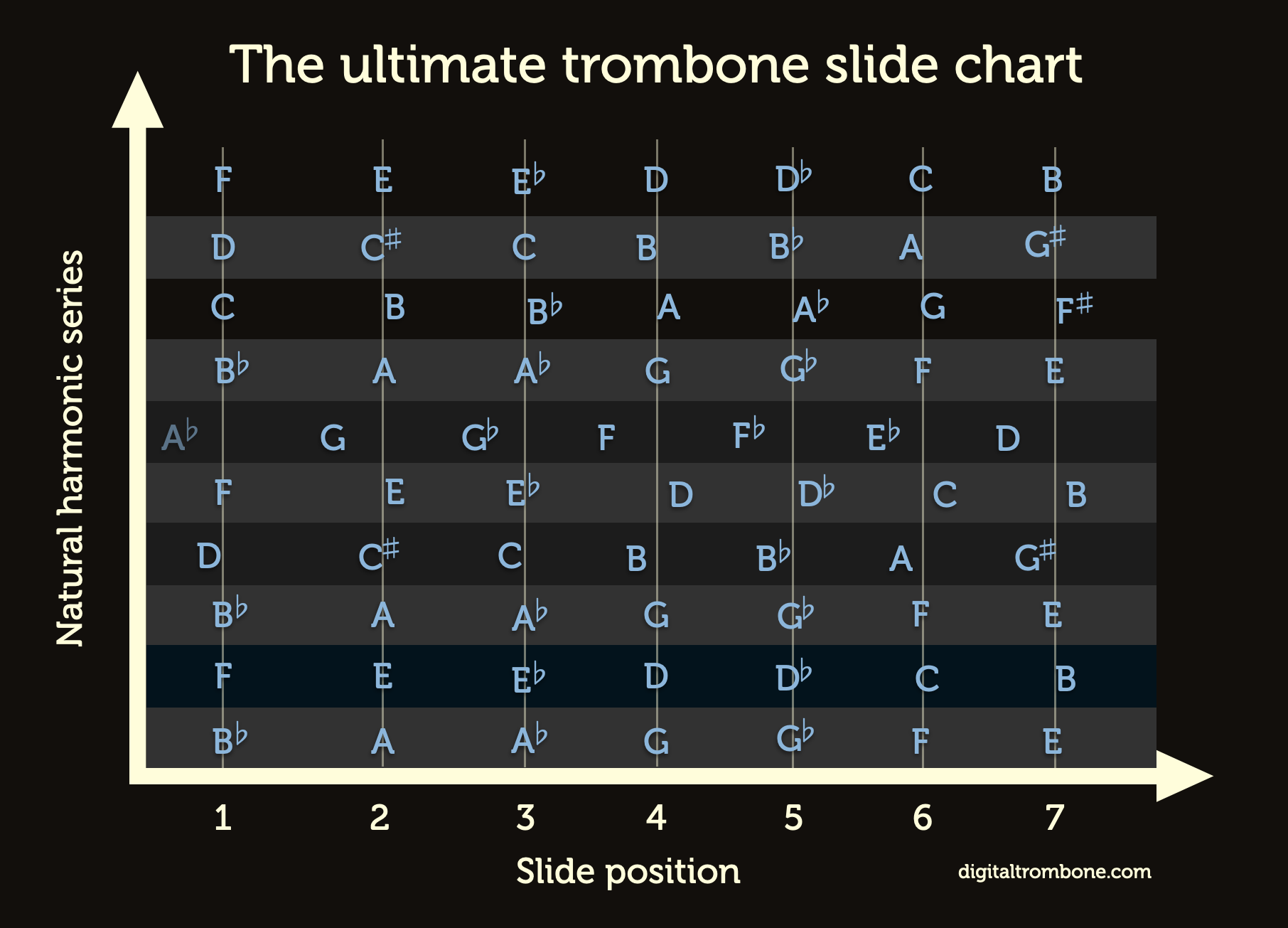
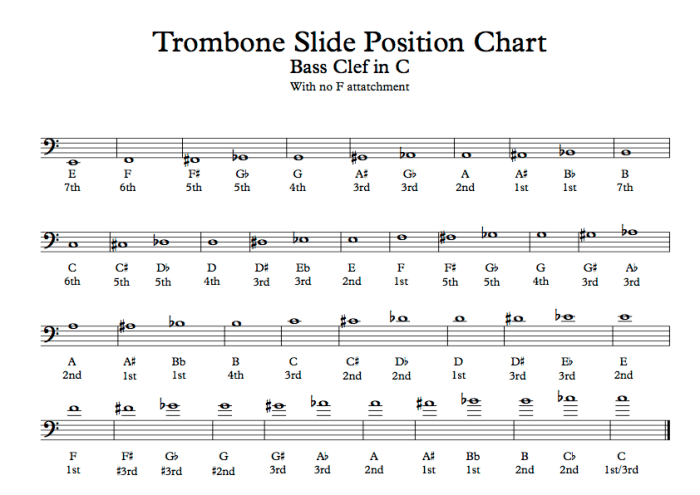
Slide Chart Analysis
Slide charts are essential tools for trigger trombone players, providing a visual representation of the slide positions required to produce specific notes. This section will delve into the organization, creation, and advantages of using a trigger trombone slide chart.
Slide Position and Note Table, Trigger trombone slide chart
A trigger trombone slide chart organizes the slide positions into a table, with each position corresponding to a specific note. The table typically includes the following information:
- Slide Position (e.g., 1st, 2nd, 3rd, etc.)
- Note Produced
- Trigger Engaged (Yes/No)
Advantages of Using a Slide Chart
Trigger trombone slide charts offer several advantages:
- Accuracy and Consistency:The chart provides precise slide positions, ensuring accurate and consistent intonation.
- Memorization Aid:By regularly using the chart, players can memorize the slide positions for different notes, improving their musical fluency.
- Efficient Practice:The chart helps players identify areas for improvement and focus their practice on specific slide positions.
- Improved Technique:The chart encourages proper slide technique, promoting smooth and controlled slide movements.
- Versatile Applications:Slide charts can be used in various musical settings, from classical to jazz and popular music.
Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance and proper care are crucial to preserving the longevity and optimal performance of your trigger trombone. Adhering to a diligent cleaning and lubrication regimen, as well as adopting preventive measures, will significantly contribute to extending the lifespan of your instrument.
Cleaning
- Regular cleaning removes dirt, moisture, and debris that can accumulate on the instrument’s surface and inside the slide. Use a soft cloth to gently wipe down the trombone after each use, paying particular attention to areas where moisture tends to gather, such as the slide and the valve casing.
- For a more thorough cleaning, disassemble the trombone and use a trombone cleaning rod with a soft brush attachment to clean the inside of the slide. Run the brush through the slide several times, rotating it as you go to ensure a thorough cleaning.
Rinse the slide with lukewarm water and dry it thoroughly with a clean cloth.
- Clean the valves regularly by removing them from the instrument and soaking them in a valve cleaning solution. Use a soft brush to gently remove any dirt or debris, then rinse the valves thoroughly with lukewarm water and dry them with a clean cloth.
Lubrication
- Lubrication reduces friction between moving parts, ensuring smooth operation and preventing wear and tear. Apply a small amount of trombone slide lubricant to the inner and outer slide tubes, as well as the valve casings. Avoid over-lubrication, as excess lubricant can attract dirt and debris.
- Use a high-quality trombone slide lubricant specifically designed for this purpose. Avoid using general-purpose lubricants, as they may contain ingredients that can damage the instrument.
- Lubricate the instrument regularly, especially after cleaning or if it has been exposed to moisture or extreme temperatures.
Preventing Common Issues
- Avoid exposing the instrument to extreme temperatures, as this can damage the metal and cause the slide to stick. If the instrument is exposed to extreme cold, allow it to warm up gradually before playing it.
- Handle the instrument with care to prevent dents or scratches. Use a sturdy case when transporting the instrument, and avoid placing it on the ground or other hard surfaces.
- Have the instrument inspected and serviced by a qualified technician on a regular basis. This will help identify and address any potential issues before they become major problems.

.gallery-container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 10px;
justify-content: center;
}
.gallery-item {
flex: 0 1 calc(33.33% – 10px); /* Fleksibilitas untuk setiap item galeri */
overflow: hidden; /* Pastikan gambar tidak melebihi batas kotak */
position: relative;
margin-bottom: 20px; /* Margin bawah untuk deskripsi */
}
.gallery-item img {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
object-fit: cover; /* Gambar akan menutupi area sepenuhnya */
object-position: center; /* Pusatkan gambar */
}
.image-description {
text-align: center; /* Rata tengah deskripsi */
}
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-item {
flex: 1 1 100%; /* Full width di layar lebih kecil dari 768px */
}
}

Our website has become a go-to destination for people who want to create personalized calendars that meet their unique needs. We offer a wide range of customization options, including the ability to add your own images, logos, and branding. Our users appreciate the flexibility and versatility of our calendars, which can be used for a variety of purposes, including personal, educational, and business use.

